K-Ras(G12C) inhibitor 12 is a co-valent and allosteric inhibitor of K-Ras G12C with potential antitumor activity. The mutated, oncogenic form of K-ras is known as KRAS G12C. K-Ras(G12C) inhibitor 12 functions by attaching itself to K-Ras(G12C) and joining forces with KRAS's 12C cysteine to form a covalent bond.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C15H17CLIN3O3 | |
| Molecular Weight | 449.67 | |
| Exact Mass | 449 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 40.07; H, 3.81; Cl, 7.88; I, 28.22; N, 9.34; O, 10.67 | |
| CAS # | 1469337-95-8 | |
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID | 73555129 | |
| Appearance | Off-white to light yellow solid powder | |
| Density | 1.736±0.06 g/cm3 | |
| Boiling Point | 680.2±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Flash Point | 365.2±31.5 °C | |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.2 mmHg at 25°C | |
| Index of Refraction | 1.674 | |
| LogP | 2.84 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 23 | |
| Complexity | 457 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 | |
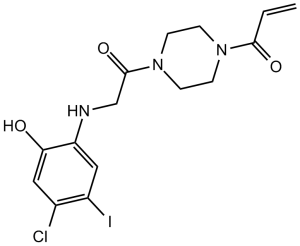
| SMILES | C=CC(N1CCN(C(CNC2=CC(I)=C(Cl)C=C2O)=O)CC1)=O |
|
| InChi Key | JFIFBWVNHLXJFY-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C15H17ClIN3O3/c1-2-14(22)19-3-5-20(6-4-19)15(23)9-18-12-8-11(17)10(16)7-13(12)21/h2,7-8,18,21H,1,3-6,9H2 | |
| Chemical Name | 1-[4-[2-(4-chloro-2-hydroxy-5-iodoanilino)acetyl]piperazin-1-yl]prop-2-en-1-one | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | K-Ras(G12C) | ||
| ln Vitro | K-Ras(G12C) inhibitor 12 is a member of a class of small molecules that binds to the common oncogenic mutant K-Ras(G12C) in an irreversible manner, preventing K-Ras(G12C) interactions. Some of them cause G12C-containing cancer cell lines to become less viable and more susceptible to apoptosis.[1] | ||
| ln Vivo |
|
||
| Cell Assay | K-Ras(G12C) inhibitor 12, an extremely potent Ras inhibitor, has an EC50 value of 0.32 μM in H1792 cells.It does not interfere with the activity of wild-type Ras; instead, it irreversibly binds to an oncogenic mutant K-Ras(G12C). K-Ras(G12C)-mutant cells show higher apoptosis and decreased viability after treatment with K-Ras(G12C) inhibitor 12 in comparison to cells without this mutation. | ||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| References |
[1]. K-Ras(G12C) inhibitors allosterically control GTP affinity and effector interactions. Nature. 2013 Nov 28;503(7477):548-551. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 1.67 mg/mL (3.71 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 16.7 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 1.67 mg/mL (3.71 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 16.7 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2239 mL | 11.1193 mL | 22.2385 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4448 mL | 2.2239 mL | 4.4477 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2224 mL | 1.1119 mL | 2.2239 mL |