Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C17H14O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 330.2889 |
| Exact Mass | 330.073 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 61.82; H, 4.27; O, 33.91 |
| CAS # | 18085-97-7 |
| Related CAS # | 18085-97-7 |
| PubChem CID | 5379096 |
| Appearance | Light yellow to yellow solid powder |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 619.0±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 232.0±25.0 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.671 |
| LogP | 1.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Complexity | 505 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
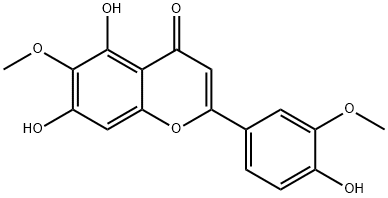
| SMILES | O1C(=C([H])C(C2C(=C(C(=C([H])C1=2)O[H])OC([H])([H])[H])O[H])=O)C1C([H])=C([H])C(=C(C=1[H])OC([H])([H])[H])O[H] |
| InChi Key | GLAAQZFBFGEBPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C17H14O7/c1-22-13-5-8(3-4-9(13)18)12-6-10(19)15-14(24-12)7-11(20)17(23-2)16(15)21/h3-7,18,20-21H,1-2H3 |
| Chemical Name | 5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-6-methoxychromen-4-one |
| Synonyms | Jaceosidin |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Bax; Mcl-1; c-FLIP; COX-2 |
| ln Vitro | After 24 hours of treatment, human kidney carcinoma Caki cells undergo disinfection induced by jaceosidin (30, 50, and 75 μM), but normal cells experience no discernible effects [1]. via suppressing NF-κB and/or Sp1 regulatory activity, Jaceosidin (75 μM) lowers MMP levels via activating Bax and releases cytochromes into Jaceosidin-induced cells to participate in Mcl-1, c-FLIP-mediated transcription [1]. In the cytoplasm of HES and HESC, jaceosidin is active [1]. After 48 hours of treatment, the inhibitory activity (IC50 values were 52.68 and 55.10 μM, respectively) and cytotoxicity (IC50 values were 70.54 and 147.14 μM, respectively) to Hec1 A and KLE were increased [2]. |
| ln Vivo | Jaceosidin (10 and 20 mg/kg, once day for three days), used as a face increases in the amount of leukocytes and protein levels in nozzle coat exudates caused by burns carrageenan [3]. Jaceosidin (20 mg/kg po every two days, hourly) lessens the volume of edema in paws that are edematous [3]. /kg, po) suppresses NF-κB activator and COX-2 expression in mice [3]. Male BALB/c mice aged 5 weeks, weighing 23–26 g [3] |
| Cell Assay |
Cell Viability Assay[2] Cell Types: Hec1A, KLE, HES and HESC Cell Tested Concentrations: 3.125, 6.25, 12.5, 25, 50 and 100 μM Incubation Duration: 48 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: demonstrated cytostatic activity against HES and HESC cells, IC50 is 52.68 and 55.10 μM, less cytotoxic Hec1 A and KLE (IC50, 70.54, 147.14 μM). |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: 5weeks old male balb/c (Bagg ALBino) mouse (23-26 g)[3] Doses: 10 and 20 mg/kg Route of Administration: P.O. one time/day for 3 days Experimental Results:diminished the volumes of exudates (inflammatory markers), cell number and protein levels. Inhibited TNF-α by 46.7% and 50.8%, IL-1β by 46.0% and 44.7%, and PGE2 by 21.7% and 16.9%, respectively, at 20 mg/kg. Blocked COX-2 expression and NF-κB activation. Animal/Disease Models: Male SD (SD (Sprague-Dawley)) rats (180-200 g)[3] Doses: 20 mg/kg Route of Administration: P.O., for 2 hour Experimental Results:diminished hind paw edema volume by 27.1% at 1 h, and 24.0% at 2 h, respectively. |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Metabolism / Metabolites Jaceosidine is a known human metabolite of eupatilin. |
| References |
[1]. Jaceosidin induces apoptosis through Bax activation and down-regulation of Mcl-1 and c-FLIP expression in human renal carcinoma Caki cells. Chem Biol Interact. 2016 Dec 25;260:168-175. [2]. Jaceosidin, isolated from dietary mugwort (Artemisia princeps), induces G2/M cell cycle arrest by inactivating cdc25C-cdc2 via ATM-Chk1/2 activation. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013 May;55:214-21. [3]. Inhibitory effect of eupatilin and jaceosidin isolated from Artemisia princeps on carrageenan-induced inflammation in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 2009 Sep 25;125(3):497-500. |
| Additional Infomation |
Jaceosidin is a trihydroxyflavone that is flavone with hydroxy groups at positions 5, 7 and 4' and methoxy groups at positions 3' and 6. Isolated from Salvia tomentosa and Artemisia asiatica, it exhibits anti-allergic, anti-inflammatory and apoptosis inducing activties. It has a role as a metabolite, an anti-inflammatory agent, an apoptosis inducer, an anti-allergic agent and an antineoplastic agent. It is a trihydroxyflavone and a dimethoxyflavone. Jaceosidin has been reported in Disynaphia multicrenulata, Stylidocleome brachycarpa, and other organisms with data available. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO: 66~125 mg/mL (199.8~378.5 mM) Ethanol: 6~7.1 mg/mL (18.2~21.6 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (6.30 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (6.30 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (6.30 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0276 mL | 15.1382 mL | 30.2764 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6055 mL | 3.0276 mL | 6.0553 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3028 mL | 1.5138 mL | 3.0276 mL |