JW-55 (JW55) is a potent and selective small molecule inhibitor of β-catenin signaling pathway with anticancer activity. It inhibits the β-catenin destruction complex regulators tankyrase 1 and tankyrase 2 (TNKS1/2) PARP domains. TNKS1/2 auto-PARsylation is reduced in vitro by JW 55, with IC50 values of 1.9 μM and 830 nM, respectively. When JW55 inhibited the poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation activity of TNKS1/2, AXIN2, a component of the β-catenin destruction complex, stabilized. This was followed by an increase in the degradation of β-catenin. In colon carcinoma cells with mutations in either the β-catenin allele or the APC (adenomatous polyposis coli) locus, JW55 inhibited canonical Wnt signaling in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, JW55 inhibited the formation of polyposis in conditional APC mutant mice induced by tamoxifen and the axis duplication induced by XWnt8 in Xenopus embryos.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C₂₅H₂₆N₂O₅ | |
| Molecular Weight | 434.48 | |
| Exact Mass | 434.184 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 69.11; H, 6.03; N, 6.45; O, 18.41 | |
| CAS # | 664993-53-7 | |
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID | 2946601 | |
| Appearance | White solid powder | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | |
| Boiling Point | 572.6±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Flash Point | 300.1±30.1 °C | |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C | |
| Index of Refraction | 1.601 | |
| LogP | 3.54 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 32 | |
| Complexity | 620 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 | |
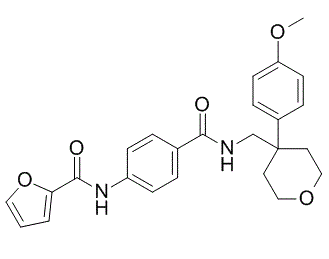
| SMILES | O1C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C(C2C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=2[H])OC([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])N([H])C(C2C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=2[H])N([H])C(C2=C([H])C([H])=C([H])O2)=O)=O)C([H])([H])C1([H])[H] |
|
| InChi Key | ZJZWZIXSGNFWQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C25H26N2O5/c1-30-21-10-6-19(7-11-21)25(12-15-31-16-13-25)17-26-23(28)18-4-8-20(9-5-18)27-24(29)22-3-2-14-32-22/h2-11,14H,12-13,15-17H2,1H3,(H,26,28)(H,27,29) | |
| Chemical Name | N-[4-[[4-(4-methoxyphenyl)oxan-4-yl]methylcarbamoyl]phenyl]furan-2-carboxamide | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | TNKS2 ( IC50 = 0.83 μM ); TNKS1 ( IC50 = 1.9 μM ) | |
| ln Vitro |
|
|
| ln Vivo |
|
|
| Enzyme Assay | JW 55, also known as JW55, is a strong and specific inhibitor of the Wnt pathway. JW55 exhibits inhibition of Wnt3a-induced HEK293 cells with an IC50 value of 470 nM, when the cells contain a transiently transfected ST-Luc (SuperTop-luciferase) reporter. JW55 exhibits efficacy within the concentration range of 1 to 5 μM in SW480 cells and 0.01 to 5 μM in HCT-15 cells. JW55 exhibits efficacy within the concentration range of 1 to 5 μM in SW480 cells and 0.01 to 5 μM in HCT-15 cells. | |
| Cell Assay | In 96-well plates, 1,000 SW480 or RKO cells are seeded. The following day, solutions containing 0.1% DMSO or 10 μM JW55 for RKO cells and 0.1% DMSO or 10, 5, or 1 μM JW55 for SW480 cells are substituted for the original cell culture medium. Every sample has at least six duplicates. Within a cell culture incubator, the plate is incubated in an IncuCyte. Every two hours, pictures are taken to track proliferation. | |
| Animal Protocol |
|
|
| References |
[1]. A novel tankyrase inhibitor decreases canonical Wnt signaling in colon carcinoma cells and reduces tumor growth in conditional APC mutant mice. Cancer Res. 2012 Jun 1;72(11):2822-32. |
|
| Additional Infomation | N-[4-[[[4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxanyl]methylamino]-oxomethyl]phenyl]-2-furancarboxamide is a member of furans and an aromatic amide. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.75 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.75 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.75 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3016 mL | 11.5080 mL | 23.0160 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4603 mL | 2.3016 mL | 4.6032 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2302 mL | 1.1508 mL | 2.3016 mL |