JNJ-632 is a novel and potent hepatitis B virus (HBV) capsid assembly modulator (CAM). Small molecule induced hepatitis B virus (HBV) capsid assembly modulation is considered an attractive approach for new antiviral therapies against HBV. JNJ-632 has been used as a tool compound to further profile the mode of action. Administration of JNJ-632 (54) in HBV genotype D infected chimeric mice resulted in a 2.77 log reduction of the HBV DNA viral load.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C18H19FN2O4S |
| Molecular Weight | 378.417866945267 |
| Exact Mass | 378.11 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 57.13; H, 5.06; F, 5.02; N, 7.40; O, 16.91; S, 8.47 |
| CAS # | 1572510-42-9 |
| PubChem CID | 73389570 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| LogP | 2.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Complexity | 595 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
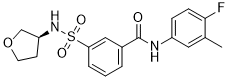
| SMILES | CC1=C(C=CC(=C1)NC(=O)C2=CC(=CC=C2)S(=O)(=O)N[C@H]3CCOC3)F |
| InChi Key | JIZGLOVJKCSHTH-HNNXBMFYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C18H19FN2O4S/c1-12-9-14(5-6-17(12)19)20-18(22)13-3-2-4-16(10-13)26(23,24)21-15-7-8-25-11-15/h2-6,9-10,15,21H,7-8,11H2,1H3,(H,20,22)/t15-/m0/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (S)-N-(4-fluoro-3-methylphenyl)-3-(N-(tetrahydrofuran-3-yl)sulfamoyl)benzamide |
| Synonyms | JNJ 632; JNJ632;JNJ-632 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | HBV |
| ln Vitro | Hepatitis B virus (HBV) inhibition is achieved by JNJ-632, a capsid assembly modulator. HBV DNA HepG2.2.15 and HBV DNA HepG2.117 are inhibited by JNJ-632, with EC50 values of 0.12 and 0.43 μM, respectively. Within the 10-30 μM range, which is regarded as weakly cytotoxic, JNJ-632 exhibits EC20s in the high-content multiparameter cytotoxicity (HepG2)[1]. |
| ln Vivo | C57BL/6 mice are used to assess the single dose PK profile of JNJ-632 after both intravenous (IV) and oral (PO) administration. JNJ-632 exhibits a moderate volume of distribution of 1.3 L/kg and a moderate plasma clearance of 34 mL/min/kg.After oral administration of 10 mg/kg, the oral bioavailability is 40%, and after oral administration of 50 mg/kg, it is 66%. With t1/2s of 0.42±0.06 h, 1.1±0.67 h, 2.4±2.3 h, and 5.3±0.1 h for 2.5 mg/kg (iv), 10 mg/kg (po), 50 mg/kg (po), and 50 mg/kg (sc), JNJ-632 has a moderate terminal elimination half-life. JNJ-632 is also administered subcutaneously to C57BL/6 mice at a dose of 50 mg/kg in order to avoid the first pass metabolism. This causes a concentration of 102 ng/mL in plasma and 1297 ng/g in the liver 24 hours after dosing[1]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Mice [1] Male C57BL/6 mice that have been fed are used to assess the pharmacokinetic profile (n=3/group). JNJ-632, formulated as a 0.5 mg/mL solution in PEG400/water (70/30), is administered intravenously (i.v.) to mice at a dose of 2.5 mg/kg. Blood is drawn from the saphenous vein at 0.05, 0.17, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 7, and 24 hours and placed into microcentrifuge tubes containing EDTA. JNJ-632 is taken orally at 10 and 50 mg/kg; it is prepared as a 0.5 and 2.5 mg/mL suspension in methocel 0.5% w/v. Blood is drawn at 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 7, 9, and 24 hours from the saphenous vein and placed into microcentrifuge tubes containing EDTA. JNJ-632 is given subcutaneously at a dose of 50 mg/kg, and blood is drawn. The plasma was kept at -20°C while the blood samples were promptly centrifuged at 4°C[1]. |
| References |
[1]. Synthesis and Evaluation of N-Phenyl-3-sulfamoyl-benzamide Derivatives as Capsid Assembly Modulators Inhibiting Hepatitis B Virus (HBV). J Med Chem. 2018 Jul 26;61(14):6247-6260. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO : 76~125 mg/mL ( 200.83~330.32 mM ) Ethanol : ~76 mg/mL |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.50 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.50 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.50 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.50 mM) (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6426 mL | 13.2128 mL | 26.4257 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5285 mL | 2.6426 mL | 5.2851 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2643 mL | 1.3213 mL | 2.6426 mL |