Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C20H37N3O13 |
| Molecular Weight | 527.52008 |
| Exact Mass | 527.232 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 45.54; H, 7.07; N, 7.97; O, 39.43 |
| CAS # | 31282-04-9 |
| PubChem CID | 20054942 |
| Appearance | White to light yellow solid powder |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 897.6±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 160-180ºC |
| Flash Point | 496.7±34.3 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.672 |
| LogP | 0.64 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 11 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 16 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 36 |
| Complexity | 756 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 14 |
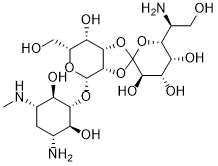
| SMILES | CN[C@H]1C[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]1O)O[C@H]2[C@@H]3[C@H]([C@H]([C@H](O2)CO)O)OC4(O3)[C@@H]([C@H]([C@H]([C@H](O4)C(CO)N)O)O)O)O)N |
| InChi Key | GRRNUXAQVGOGFE-HUCHGKBZSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C20H37N3O13/c1-23-7-2-5(21)9(26)15(10(7)27)33-19-17-16(11(28)8(4-25)32-19)35-20(36-17)18(31)13(30)12(29)14(34-20)6(22)3-24/h5-19,23-31H,2-4,21-22H2,1H3/t5-,6+,7+,8-,9+,10-,11+,12-,13+,14-,15-,16+,17+,18-,19+,20?/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | D-Streptamine, O-6-amino-6-deoxy-L-glycero-D-galacto-heptopyranosylidene(1-2-3)-O-beta-D-talopyranosyl-(1->)-2-deoxy-N3-methyl- |
| Synonyms | HygromycinB, Hygrovetine, Hygromix 2.4, Antihelmycin, Hygromix-8;Hygromycin-B; AI3-29796; hygromycin b; 31282-04-9; Hygrovetine; MFCD06795479; (2S,3R,3A'S,4S,4'S,5R,6R,6'R,7'S,7a'S)-4'-(((1R,2S,3R,5S,6R)-3-amino-2,6-dihydroxy-5-(methylamino)cyclohexyl)oxy)-6-((R)-1-amino-2-hydroxyethyl)-6'-(hydroxymethyl)octahydro-4'H-spiro[pyran-2,2'-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-c]pyran]-3,4,5,7'-tetraol; 1217468-11-5; C20H37N3O13; CHEMBL4647156; AI3 29796; AI329796 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.03.00 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Aminoglycoside |
| ln Vitro | Streptomyces hygroscopicus synthesizes hygromycin B, an aminocyclitol antibiotic that strongly inhibits both 70S and 80S ribosomes[1]. At a concentration of 0.38 mM, hygromycin B completely stops the growth of yeast cells in rich media, most likely by stopping cytoplasmic ribosomes from synthesizing proteins. Low concentrations of hygromycin B significantly inhibit the synthesis of polypeptides in cell-free extracts from yeast, wheat germ, and rabbit reticulocytes. The antibiotic stops the translocation of elongation factor EF-2, which inhibits yeast polysomes from elongating peptide chains. Hygromycin B's suppression of translocation may be due to the stabilization of peptidyl-tRNA attached to the ribosomal acceptor site[2]. |
| ln Vivo |
By preventing ribosome translocation, hygromycin B inhibits protein synthesis without significantly altering ribosome positioning in vivo[3]. Hygromycin B resistance is conferred in vivo in transgenic mice through constitutive expression of the bacterial hygR gene[4]. |
| Enzyme Assay |
Hygromycin B is an aminoglycoside antibiotic active against prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes. Ribosomal alterations in bacteria conferring resistance to hygromycin B have not been described, prompting us to use a single rRNA allelic derivative of the gram-positive bacterium Mycobacterium smegmatis for investigation of the molecular mechanisms involved in ribosomal resistance to hygromycin B in eubacteria. Resistance mutations were found to localize exclusively in 16S rRNA. The mutations observed, i.e., 16S rRNA U1406C, C1496U, and U1498C (E. coli numbering), are in close proximity to the hygromycin B binding site located in conserved helix 44 of 16S rRNA. The 16S rRNA positions involved in hygromycin B resistance are highly conserved in all three domains of life, explaining the lack of specificity and general toxicity of hygromycin B[3]. Hygromycin B, an aminocyclitol antibiotic that strongly inhibits both 70S and 80S ribosomes, is synthesized by Streptomyces hygroscopicus. Ribosomes from this Gram-positive mycelial bacterium are inhibited in vitro by the antibiotic. In contrast, the streptomycete is highly resistant to the drug in vivo since it possesses hygromycin B phosphotransferase activity. This enzyme has been shown by gel filtration to have a molecular weight of 42000, and to modify its antibiotic substrate to produce 7"-O-phosphoryl-hygromycin B which totally lacks biological activity both in vivo and in vitro[1]. |
| Cell Assay | Hygromycin B is an unusual aminoglycoside antibiotic active against both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Hygromycin B at 0.38 mM concentration completely halts yeast cell growth in rich media, presumably by preventing protein synthesis by cytoplasmic ribosomes. Polypeptide synthesis in cell-free extracts from rabbit reticulocytes, wheat germ and yeast is strongly blocked by low concentrations of hygromycin B. The antibiotic inhibits peptide chain elongation by yeast polysomes by preventing elongation factor EF-2-dependent translocation, although it does not affect either the formation of the EF-2-GTP-ribosome complex or the EF-2- and ribosome-dependent GTP hydrolysis which takes place uncoupled from translocation. The inhibition of translocation by hygromycin B might result from the stabilization of peptidyl-tRNA bound to the ribosomal acceptor site, since the stability of [3H]Phe-tRNA-EF-1-poly(U)-ribosome and [3H]Phe-tRNA-poly(U)-ribosome complexes is increased in the presence of hygromycin B. The inhibition of polyphenylalanine synthesis by reticulocyte ribosomes and enzymic translocation of peptidyl-tRNA by yeast polysomes can be reversed by increasing concentrations of EF-2 suggesting a relationship between the binding sites of EF-2 and hygromycin B on the ribosome. Neither non-enzymic translocation, that takes place in the presence of high potassium concentrations, nor the peptide bondforming step are affected by hygromycin B[2]. |
| Animal Protocol | Dissolve hygromycin B in sterile water. Hygromycin B i.p. is administered as a single dose to the hygR-carrying C57BL/6J-TgN(pPWL512hyg)1Em mice at a starting dose of 2.7 mg/kg and increasing by 50% with each subsequent dose. The same volume of sterile saline is administered to wild-type C57BL/6J control mice. There is 0.5 mL injected in total. For ten days in a row, the animals' body weight and general health are observed every day[4]. |
| References |
[1]. Biochemical basis of resistance to hygromycin B in Streptomyces hygroscopicus--the producing organism. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Jun;131(6):1289-98. [2]. Studies on the mode of action of hygromycin B, an inhibitor of translocation in eukaryotes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 21;521(2):459-69. [3]. Role of 16S rRNA Helix 44 in Ribosomal Resistance to Hygromycin B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003 May;47(5):1496-502. |
| Additional Infomation |
Amorphous solid or tan powder. (NTP, 1992) Hygromycin B is an aminoglycoside antibiotic produced by the bacterium Streptomyces hygroscopicus which kills bacteria, fungi and higher eukaryotic cells by inhibiting protein synthesis. Aminoglycoside produced by Streptomyces hygroscopicus. It is used as an anthelmintic against swine infections by large roundworms, nodular worms, and whipworms. See also: Hygromycin B (annotation moved to). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~189.57 mM ) H2O : 50~100 mg/mL (~94.78 mM ) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 5 mg/mL (9.48 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 50.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 5 mg/mL (9.48 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 50.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 5 mg/mL (9.48 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 50.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.74 mM) (saturation unknown) in 5% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 50% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 5: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.74 mM) (saturation unknown) in 5% DMSO + 95% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 6: ≥ 0.5 mg/mL (0.95 mM) (saturation unknown) in 1% DMSO 99% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 7: 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: ≥ 5 mg/mL (9.48 mM) Solubility in Formulation 8: 100 mg/mL (189.57 mM) in PBS (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with ultrasonication. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8957 mL | 9.4783 mL | 18.9566 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3791 mL | 1.8957 mL | 3.7913 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1896 mL | 0.9478 mL | 1.8957 mL |