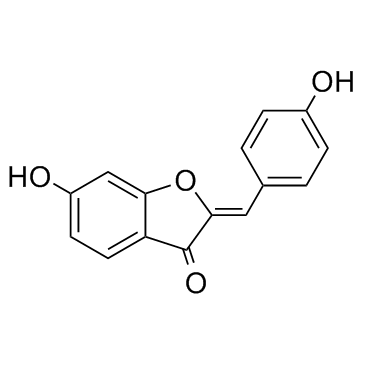
Hispidol ((Z)-Hispidol) is a potential therapeutic for inflammatory bowel disease; which has an IC50 of 0.50 M and inhibits TNF-induced monocyte adhesion to colon epithelial cells.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C15H10O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 254.2375 |
| Exact Mass | 254.058 |
| CAS # | 5786-54-9 |
| Related CAS # | 5786-54-9 |
| PubChem CID | 5281254 |
| Appearance | Light yellow to yellow solid |
| Density | 1.489g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 523.8ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 288 °C |
| Flash Point | 205.7ºC |
| Index of Refraction | 1.755 |
| LogP | 2.714 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Complexity | 382 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| SMILES | O1/C(=C(/[H])\C2C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=2[H])O[H])/C(C2C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C1=2)O[H])=O |
| InChi Key | KEZLDSPIRVZOKZ-AUWJEWJLSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C15H10O4/c16-10-3-1-9(2-4-10)7-14-15(18)12-6-5-11(17)8-13(12)19-14/h1-8,16-17H/b14-7- |
| Chemical Name | (2Z)-6-hydroxy-2-[(4-hydroxyphenyl)methylidene]-1-benzofuran-3-one |
| Synonyms | Hispidol; (Z)-Hispidol |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | Hispidol shows potent inhibitory effect (>70%) on the TNF-α-induced adhesion of monocytes to colon epithelial cells, which is one of the hallmark events leading to inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Hispidol is a strong candidate for the development of IBD medications due to its potent inhibitory effects against TNF-α induced monocytic-colonic epithelial cell adhesion as well as LPS-induced TNF-α expression. Hispidol inhibits the transcription of AP-1, a transcription factor also necessary for high levels of TNF-α expression, which corresponds to the additional inhibitory activity against AP-1 transcriptional activity[1]. |
| ln Vivo | Hispidol is an oral drug that significantly and dose-dependently inhibits TNBS-induced rat colitis. A dose-dependent response is seen when hispidol is administered orally to treat TNBS-induced colitis. Body weight loss and colon tissue edematous inflammation have significantly improved. Hispidol, at a higher dose of 30 mg/kg, has a recovery effect comparable to sulfasalazine, at a dose of 300 mg/kg. Hispidol significantly reduces MPO, a biochemical marker of inflammation, in a dose-dependent manner in the colon tissues after TNBS causes a dramatic rise in its level[1]. |
| References |
[1]. Discovery and structure-activity relationship studies of 2-benzylidene-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-one and benzofuran-3(2H)-one derivatives as a novel class of potential therapeutics for inflammatory bowel disease. Eur J Med Chem. 2017 Sep 8. |
| Additional Infomation |
Hispidol is a hydroxyaurone that is aurone substituted by hydroxy groups at positions 6 and 4' respectively. It has a role as a plant metabolite. It is functionally related to an aurone. Hispidol has been reported in Glycine max and Retama raetam with data available. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: ≥100 mg/mL (~393.3 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.9333 mL | 19.6665 mL | 39.3329 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7867 mL | 3.9333 mL | 7.8666 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3933 mL | 1.9666 mL | 3.9333 mL |