HA14-1 is a novel, potent and non-peptidic inhibitor of a B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) surface pocket with IC50 of ~9 μM. By imitating the BH3 domain necessary for the formation of homo- and hetero-dimers, HA14-1 binds to Bcl-2 and inhibits Bcl-2 by blocking the binding of these proteins. HA14-1 has received a lot of attention in apoptosis research, which makes it more promising as a cancer treatment.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C17H17BRN2O5 | |
| Molecular Weight | 409.23 | |
| Exact Mass | 408.032 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 49.89; H, 4.19; Br, 19.53; N, 6.85; O, 19.55 | |
| CAS # | 65673-63-4 | |
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID | 3549 | |
| Appearance | White to light yellow solid powder | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | |
| Boiling Point | 535.1±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Melting Point | 105ºC | |
| Flash Point | 277.4±30.1 °C | |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C | |
| Index of Refraction | 1.574 | |
| LogP | 3.7 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 25 | |
| Complexity | 611 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 | |
| SMILES | BrC1C([H])=C([H])C2=C(C=1[H])C([H])(C(C(=O)OC([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])=C(N([H])[H])O2)C([H])(C#N)C(=O)OC([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] |
|
| InChi Key | SXJDCULZDFWMJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C17H17BrN2O5/c1-3-23-16(21)11(8-19)13-10-7-9(18)5-6-12(10)25-15(20)14(13)17(22)24-4-2/h5-7,11,13H,3-4,20H2,1-2H3 | |
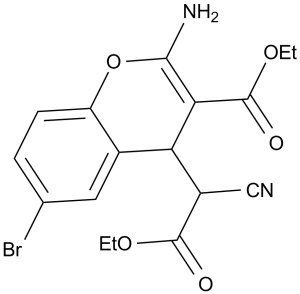
| Chemical Name | ethyl 2-amino-6-bromo-4-(1-cyano-2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Bcl-2 (IC50=9 μM ); Bcl-xL | ||
| ln Vitro | HA14-1 is a nonpeptidic ligand of a Bcl-2 surface pocket. Apaf-1 and caspases are activated by HA14-1, possibly by binding to the Bcl-2 protein and preventing it from performing its intended function. As a series of synthetic analogs derived from HA14-1 containing various modifications are found to have greatly different Bcl-2 binding activities, it appears that the interaction of HA14-1 with the Bcl-2 surface pocket is specific for the chemical structure of HA14-1. HL-60 cells are exposed to various concentrations of HA14-1 for 4 hours in order to investigate the impact of HA14-1 on cell viability. HL-60 cells are killed by HA14-1 in a dose-dependent manner. More than 90% of the cells lose viability at a concentration of 50 M of HA14-1[1]. HA14-1 is a Bcl-2/Bcl-xL antagonist[2]. | ||
| ln Vivo | Swiss nude mice injected with human glioblastoma multiforme cells are also given i.p. low doses of Etoposide (2.5 mg/kg in 200 L of 0.9% NaCl 5 days a week starting on day 2 after cell injection) along with HA14-1 or mock treatment to examine whether HA14-1 treatment might increase the efficacy of another antitumoral treatment. Etoposide treatment is insufficient to stop the growth of glioblastoma cells on its own, but when combined with HA14-1, it significantly slows tumor growth, as shown by the ability of the combined therapy to lengthen the tumor volume's time to double[3]. | ||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| References |
[1]. Structure-based discovery of an organic compound that binds Bcl-2 protein and induces apoptosis of tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Jun 20;97(13):7124-9. [2]. Initiation of apoptosis and autophagy by the Bcl-2 antagonist HA14-1. Cancer Lett. 2007 May 8;249(2):294-9. [3]. The small organic compound HA14-1 prevents Bcl-2 interaction with Bax to sensitize malignant glioma cells to induction of cell death. Cancer Res. 2006 Mar 1;66(5):2757-64. . |
||
| Additional Infomation | 2-amino-6-bromo-4-(1-cyano-2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester is a 1-benzopyran. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.11 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.11 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 3: 1% DMSO+30% polyethylene glycol+1% Tween 80: 30mg/mL (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4436 mL | 12.2181 mL | 24.4361 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4887 mL | 2.4436 mL | 4.8872 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2444 mL | 1.2218 mL | 2.4436 mL |