Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C₆₀H₁₀₁N₁₅O₁₇ |
| Molecular Weight | 1304.53 |
| Exact Mass | 1303.75 |
| CAS # | 198284-64-9 |
| PubChem CID | 9920128 |
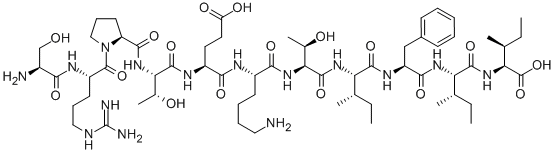
| Sequence | Ser-Arg-Pro-Thr-Glu-Lys-Thr-Ile-Phe-Ile-Ile |
| SequenceShortening | SRPTEKTIFII |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| LogP | 2.192 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 18 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 20 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 42 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 92 |
| Complexity | 2480 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 16 |
| SMILES | CC[C@H](C)[C@@H](C(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H](C)CC)C(=O)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CC1=CC=CC=C1)NC(=O)[C@H]([C@@H](C)CC)NC(=O)[C@H]([C@@H](C)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CCCCN)NC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)[C@H]([C@@H](C)O)NC(=O)[C@@H]2CCCN2C(=O)[C@H](CCCN=C(N)N)NC(=O)[C@H](CO)N |
| InChi Key | SXRAPDIXXYFGJG-MDAHIHQXSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C60H101N15O17/c1-9-31(4)44(54(86)69-41(29-36-19-13-12-14-20-36)52(84)70-45(32(5)10-2)55(87)72-46(59(91)92)33(6)11-3)71-57(89)48(35(8)78)73-51(83)38(21-15-16-26-61)66-50(82)39(24-25-43(79)80)67-56(88)47(34(7)77)74-53(85)42-23-18-28-75(42)58(90)40(22-17-27-65-60(63)64)68-49(81)37(62)30-76/h12-14,19-20,31-35,37-42,44-48,76-78H,9-11,15-18,21-30,61-62H2,1-8H3,(H,66,82)(H,67,88)(H,68,81)(H,69,86)(H,70,84)(H,71,89)(H,72,87)(H,73,83)(H,74,85)(H,79,80)(H,91,92)(H4,63,64,65)/t31-,32-,33-,34+,35+,37-,38-,39-,40-,41-,42-,44-,45-,46-,47-,48-/m0/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (2S,3S)-2-[[(2S,3S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S,3S)-2-[[(2S,3R)-2-[[(2S)-6-amino-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S,3R)-2-[[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-amino-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)pentanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carbonyl]amino]-3-hydroxybutanoyl]amino]-4-carboxybutanoyl]amino]hexanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxybutanoyl]amino]-3-methylpentanoyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoyl]amino]-3-methylpentanoyl]amino]-3-methylpentanoic acid |
| Synonyms | Gap27 Gap-27Gap 27 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | Gap 27 resulted in a considerable reduction in the number of TRAP-positive mononuclear and multinucleated osteoclasts grown on bovine bone slices. By quantifying the percentage of osteoclasts with actin rings among all TRAP-positive cells, it was found that the surviving osteoclasts and the resorption area were considerably reduced in the treated cultures [1]. Connecting the lumbar carotid artery with a stent equivalent to Gap 27 (500 μM) substantially removed ULC on cervical choline but had no effect on levcromakalim. In isolated guinea pig internal carotid arteries, Gap 27 prevents endothelial-supported ultrashort circuits of choline induction [2]. |
| ln Vivo | The relaxation of the superior mesenteric artery and thoracic aorta is 40% inhibited by gap 27 (300 μM). In the thoracic aorta, gap 27 also inhibits the relaxation endothelium-dependent aspect of ATP sensing [3]. |
| References |
[1]. Connexin-mimetic peptide Gap 27 decreases osteoclastic activity. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2001;2:10. [2]. Role of gap junctions in the responses to EDHF in rat and guinea-pig small arteries. Br J Pharmacol. 1999 Dec;128(8):1788-94. [3]. Chaytor AT,e t al. Central role of heterocellular gap junctional communication in endothelium-dependent relaxations of rabbit arteries. J Physiol. 1998 Apr 15;508 ( Pt 2):561-73. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO : ~50 mg/mL (~38.33 mM) 0.1 M HCL : 50 mg/mL (~38.33 mM) H2O : ~26.32 mg/mL (~20.18 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.7666 mL | 3.8328 mL | 7.6656 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.1533 mL | 0.7666 mL | 1.5331 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.0767 mL | 0.3833 mL | 0.7666 mL |