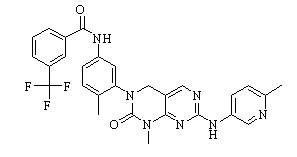
GNF-7 (GNF7; GNF 7) is a novel, potent, orally bioactive/bioavailable Bcr-Abl kinase inhibitor with potential anticancer activity. It inhibits the following kinases: M351T, T315I, E255 V, G250E and c-Abl, with IC50s of<5 nM, 61 nM, 122 nM, 136 nM, and 133 nM, respectively. It demonstrate significant in vivo antitumor efficacy in SCID beige female mice bearing T315I-Bcr-Abl-Ba/F3 orthotopic xenografts.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C28H24F3N7O2 | |
| Molecular Weight | 547.53 | |
| Exact Mass | 547.194 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 61.42; H, 4.42; F, 10.41; N, 17.91; O, 5.84 | |
| CAS # | 839706-07-9 | |
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID | 11478363 | |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | |
| Index of Refraction | 1.655 | |
| LogP | 2.78 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 40 | |
| Complexity | 908 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 | |
| SMILES | O=C(C1C=C(C(F)(F)F)C=CC=1)NC1C=C(N2CC3C(=NC(NC4C=CC(C)=NC=4)=NC=3)N(C)C2=O)C(C)=CC=1 |
|
| InChi Key | SZNYUUZOQHNEKB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C28H24F3N7O2/c1-16-7-9-21(34-25(39)18-5-4-6-20(11-18)28(29,30)31)12-23(16)38-15-19-13-33-26(36-24(19)37(3)27(38)40)35-22-10-8-17(2)32-14-22/h4-14H,15H2,1-3H3,(H,34,39)(H,33,35,36) | |
| Chemical Name | N-(4-methyl-3-(1-methyl-7-((6-methylpyridin-3-yl)amino)-2-oxo-1,4-dihydropyrimido[4,5-d]pyrimidin-3(2H)-yl)phenyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | Bcr-Abl mutants such T315I (IC50=11 nM), G250E (IC50<5 nM), E255V (IC50=10 nM), F317L (IC50<5 nM), and M351T (IC<5 nM) sub>50<5 nM) are all efficiently inhibited by GNF-7[2]. AKT/mTOR signaling is inhibited and GCK downstream by GNF-7 (1 μM; 2 hours) [3]. In NRAS mutant cell lines, GNF-7 (1 μM; 24 hours) causes apoptosis and cell cycle arrest [3]. |
| ln Vivo | In a bioluminescent xenograft mouse model, GNF-7 (10–20 mg/kg; op; daily; for 7 days) showed notable in vivo effectiveness against T315I Bcr-Abl [2]. GNF-7 has a limited oral bioavailability (36% in mice) and Cmax (3616 nM in mice) following oral treatment (20 mg/kg) [2]. Because GNF-7 has a high plasma clearance rate (8.6 mL/min/kg) following intravenous injection (5 mg/kg in mice), it has a terminal elimination half-life of 3.8 hours in mice [2]. |
| Cell Assay |
Western Blot Analysis[3] Cell Types: Ba/F3-NRAS-G12D cells, OCI-AML3 cells Tested Concentrations: 1 μM Incubation Duration: 2 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Caused a diminished level of phosphorylation of p70S6K1, AKT (S473), JNK, and p38. Apoptosis Analysis[3] Cell Types: OCI-AML3 cells Tested Concentrations: 1 μM Incubation Duration: 24 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Increased the levels of both cleaved PARP and cleaved caspase 3 and diminished bcl-2 and MCL1. Cell Cycle Analysis[3] Cell Types: OCI-AML3 cells Tested Concentrations: 1 μM Incubation Duration: 24 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Induced of G0-G1 arrest. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: 6-8 weeks old SCID beige female mice, with Ba/F3-T315I-Bcr-Abl cells xenograft[2] Doses: 10 mg/kg, 20 mg/kg Route of Administration: Oral administration, daily, for 7 days Experimental Results: Effectively inhibited tumor growth of T315I-Bcr-Abl-Ba/F3 cells in mice at low doses (10 mg/kg). Animal/Disease Models: 5-6 weeks old male balb/c (Bagg ALBino) mouse (20-25 g)[2] Doses: 5 mg/kg for iv; 20 mg/kg for ig (pharmacokinetic/PK Analysis) Route of Administration: intravenous (iv) injection and po (oral gavage) Experimental Results: Oral bioavailability (36%), Cmax (3616 nM), T1/2 (3.2 h). |
| References |
[1]. Hybrid pyrimidine alkynyls inhibit the clinically resistance related Bcr-Abl(T315I) mutant. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015 Sep 1;25(17):3458-63. [2]. A type-II kinase inhibitor capable of inhibiting the T315I "gatekeeper" mutant of Bcr-Abl. J Med Chem. 2010 Aug 12;53(15):5439-48. [3]. First SAR study for overriding NRAS mutant driven acute myeloid leukemia. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2 mg/mL (3.65 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2 mg/mL (3.65 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8264 mL | 9.1319 mL | 18.2638 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3653 mL | 1.8264 mL | 3.6528 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1826 mL | 0.9132 mL | 1.8264 mL |