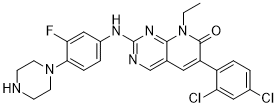
FRAX486 is a novel and potent p21-activated kinase (PAK) inhibitor (IC50 are 14, 33, 39 and 575 nM for PAK1, PAK2, PAK3 and PAK4 respectively). The hypothesis that a medication therapy that reverses the abnormalities in the spine can also treat neurological and behaviorally bioavailable symptoms is supported by the fact that FRAX486 rescues seizures and behaviorally bioavailable abnormalities like hyperactivity and repetitive movements. All of these phenotypes can be restored with a single administration of FRAX486 in adult Fmr1 KO mice, suggesting that postdiagnostic therapy for adults with FXS may be initiated quickly. In vitro and in vivo, FRAX486 reduces the degeneration of the dendritic spine linked to schizophrenia in late adolescence.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C25H23CL2FN6O |
| Molecular Weight | 513.4 |
| Exact Mass | 512.129 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 58.49; H, 4.52; Cl, 13.81; F, 3.70; N, 16.37; O, 3.12 |
| CAS # | 1232030-35-1 |
| Related CAS # | 1232030-35-1 |
| PubChem CID | 68060125 |
| Appearance | Light yellow to yellow solid powder |
| LogP | 4.893 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 35 |
| Complexity | 783 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| SMILES | FC1=CC(NC2=NC=C3C(N(CC)C(C(C4=CC=C(Cl)C=C4Cl)=C3)=O)=N2)=CC=C1N5CCNCC5 |
| InChi Key | DHKFOIHIUYFSOF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C25H23Cl2FN6O/c1-2-34-23-15(11-19(24(34)35)18-5-3-16(26)12-20(18)27)14-30-25(32-23)31-17-4-6-22(21(28)13-17)33-9-7-29-8-10-33/h3-6,11-14,29H,2,7-10H2,1H3,(H,30,31,32) |
| Chemical Name | 6-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-8-ethyl-2-(3-fluoro-4-piperazin-1-ylanilino)pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-one |
| Synonyms | FRAX486; FRAX 486; FRAX-486 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | PAK1 (IC50 = 14 nM); PAK2 (IC50 = 33 nM); PAK3 (IC50 = 39 nM); PAK4 (IC50 = 575 nM) |
| ln Vitro | FRAX486 causes concentration-dependent (1–10 μM) actin filament degeneration in WPMY-1 cells. Attenuation of the proliferation rate was also observed between 1 and 10 μM FRAX486. In WPMY-1 cells, FRAX486's cytotoxicity is concentration- and time-dependent. FRAX486 had effects on actin organization, survival, and proliferation in WPMY-1 cells as early as 1–5 μM. While only partial inhibition of PAK4 may occur at these concentrations, complete inhibition of PAK1-3 may be anticipated[2]. |
| ln Vivo | FRAX486 is able to penetrate the blood-brain barrier. It can reach the brain as early as 1 hour after administration and stay there for up to 24 hours.Its maximum concentration in the target tissue is reached after 8 hours. FRAX486 levels in the brain stabilize after daily dosing. Instead of just decreasing spine density regardless of genotype or phenotypic presence, FRAX486 specifically rescues the Fmr1 KO abnormality, in which the spine phenotype is present in apical neurons. Moreover, FRAX486 lessens stereotypical movements and hyperactivity, two traits that define the mouse model of fragile X syndrome[3]. |
| Cell Assay | WPMY-1 cells are plated on a coverslip with 16 wells and a density of 50,000/well. Cells are treated with FRAX486 (1, 5, 10 μM), IPA3 (1, 5, 10 μM), or DMSO after a 24-hour period. A further twenty-four hours later, the medium is swapped out for a 10-mM 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EdU) solution in an FCS-free medium that contains solvent or inhibitors. Cells were fixed with 3.7% formaldehyde 20 hours later. Utilizing the "EdU-Click 555" cell proliferation assay, EdU incorporation is studied. The assay measures the amount of EdU incorporated into DNA by using fluorescing 5-carboxytetramethylrhodamine (5-TAMRA) to detect the incorporation. Every nucleus is counterstained using DAPI. Fluorescence microscopy is used to examine cells (emission: 479 nm; excitation: 546 nm). |
| Animal Protocol | Mice: There are male C57BL/6 mice that are fasted. When it comes to FRAX486, the intravenous (IV) dose is 3 mg/kg with a 1 mg/mL solution in 20% (wt/vol) 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin in water, and the oral (PO) dose is 30 mg/kg with a 3 mg/mL solution in water. In the in vivo trial, FRAX486 is injected intraperitoneally [10 μg/BW (g)] once daily between P35 and P60, resulting in brain concentrations greater than 175 nM. |
| References |
[1]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 2014 Apr 29;111(17):6461-6. [2]. PLoS One . 2016 Apr 12;11(4):e0153312. [3]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 2013 Apr 2;110(14):5671-6. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: 21.2~30 mg/mL (41.3~58.4 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9478 mL | 9.7390 mL | 19.4780 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3896 mL | 1.9478 mL | 3.8956 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1948 mL | 0.9739 mL | 1.9478 mL |