Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C27H33CL2FN4O8 |
| Molecular Weight | 631.48 |
| Exact Mass | 630.165 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 51.36; H, 5.27; Cl, 11.23; F, 3.01; N, 8.87; O, 20.27 |
| CAS # | 1334714-66-7 |
| Related CAS # | Eravacycline;1207283-85-9 |
| PubChem CID | 56951485 |
| Appearance | Light yellow to yellow solid powder |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 11 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 42 |
| Complexity | 1200 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
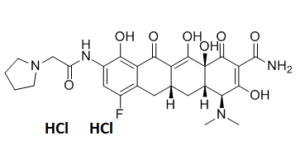
| SMILES | Cl.Cl.FC1=CC(=C(C2=C1C[C@@H]1C(=C2O)C([C@@]2(C(=C(C(N)=O)C([C@H]([C@@H]2C1)N(C)C)=O)O)O)=O)O)NC(CN1CCCC1)=O |
| InChi Key | JYCNMRVZELJVAW-RZVFYPHASA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C27H31FN4O8.2ClH/c1-31(2)20-13-8-11-7-12-14(28)9-15(30-16(33)10-32-5-3-4-6-32)21(34)18(12)22(35)17(11)24(37)27(13,40)25(38)19(23(20)36)26(29)39;;/h9,11,13,20,34,36-37,40H,3-8,10H2,1-2H3,(H2,29,39)(H,30,33);2*1H/t11-,13-,20-,27-;;/m0../s1 |
| Chemical Name | (4S,4aS,5aR,12aS)-4-(Dimethylamino)-7-fluoro-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-9-((pyrrolidin-1-ylacetyl)amino)-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydrotetracene-2-carboxamide dihydrochloride |
| Synonyms | TP-434-046; TP 434-046; TP434-046; TP-434; TP 434; TP434; Eravacycline HCl; Eravacycline hydrochloride. |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: (1). This product requires protection from light (avoid light exposure) during transportation and storage.(2). Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment (e.g. under nitrogen), avoid exposure to moisture.(3). This product is not stable in solution, please use freshly prepared working solution for optimal results. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | Strong antibiotic eryavacycline is effective against isolates of A. baumannii, including those resistant to sulbactam, BAY 41-6551, and SM 7338. Eravacycline is more active than colistin and BAY 41-6551. The MIC50/90 values of eravacycline dihydrochloride are 0.5/1 mg/L [1]. Six E. coli strains with MICs ranging from 0.125 to 0.25 mg/L exhibit inhibitory effects when exposed to eravacycline[2]. Eravacycline dihydrochloride is a synthetic antibiotic that binds to the 30S ribosomal subunit to prevent bacteria from synthesizing proteins. Eravacycline exhibits good activity against significant gram-positive pathogens, such as methicillin-resistant S. aureus, and broad spectrum activity against gram-negative bacteria in the panel, with the exception of P. aeruginosa. Additionally, eravacycline exhibits strong ribosomal inhibition[3].In all species panels, eravacycline exhibits strong broad-spectrum activity against 90% of the isolates (MIC90) at concentrations ranging from ≤0.008 to 2 μg/mL, with the exception of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia cenocepacia, which both have MIC90 values of 32 μg/mL. Eravacycline exhibits efficacy against bacteria that are resistant to multiple drugs, such as those that express extended-spectrum β-lactamases and mechanisms that confer resistance to other antibiotic classes, such as carbapenem resistance[4]. |
| ln Vivo | Several murine infection models demonstrate the efficacy of eravacycline dihydrochloride against Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens that are clinically significant. Eravacycline shows 50% protective dose values of ≤1 mg/kg of body weight once a day (q.d.) against Staphylococcus aureus in mouse septicemia models, indicating its effectiveness. In relation to Escherichia coli isolates, the PD50 values range from 1.2 to 4.4 mg/kg q.d[5]. |
| Animal Protocol | Rats: Sprague-Dawley rats are used to determine pharmacokinetic (PK) parameters. After fasting for at least 12 hours, the animals receive a single oral dose of eravacycline (10 mg/kg) or an IV dose (1 mg/kg), and then they participate in a 24-hour sampling scheme. Using the relevant standard curves, TurboIonspray LC/MSMS analysis determines the concentrations of the dosing solution and plasma. Noncompartmental analysis is used to calculate PK parameters[3]. |
| References |
[1]. In-vitro activity of the novel fluorocycline eravacycline against carbapenem non-susceptible Acinetobacter baumannii. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2017 Jul 10. [2]. In Vivo Pharmacodynamic Target Assessment of Eravacycline against Escherichia coli in a Murine Thigh Infection Model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Jun 27;61(7). [3]. Fluorocyclines: a potent, broad spectrum antibacterial agent. J Med Chem. 2012 Jan 26;55(2):597-605. [4]. Antibacterial activity of eravacycline (TP-434), a novel fluorocycline, against hospital and community pathogens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Nov;57(11):5548-58. [5]. Eravacycline (TP-434) is efficacious in animal models of infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 May;59(5):2567-71. |
| Additional Infomation | See also: Eravacycline Dihydrochloride (annotation moved to). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
H2O : ~100 mg/mL (~158.36 mM) DMSO : ≥ 50 mg/mL (~79.18 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 5.5 mg/mL (8.71 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 55.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 5.5 mg/mL (8.71 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 55.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 5.5 mg/mL (8.71 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 55.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: ≥ 5.5 mg/mL (8.71 mM) Solubility in Formulation 5: 50 mg/mL (79.18 mM) in PBS (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with ultrasonication. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.5836 mL | 7.9179 mL | 15.8358 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3167 mL | 1.5836 mL | 3.1672 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1584 mL | 0.7918 mL | 1.5836 mL |