Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C14H16N2O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 276.29 |
| Exact Mass | 276.111 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 60.86; H, 5.84; N, 10.14; O, 23.16 |
| CAS # | 104421-21-8 |
| PubChem CID | 9882056 |
| Appearance | Solid powder |
| LogP | 1.806 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 20 |
| Complexity | 402 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
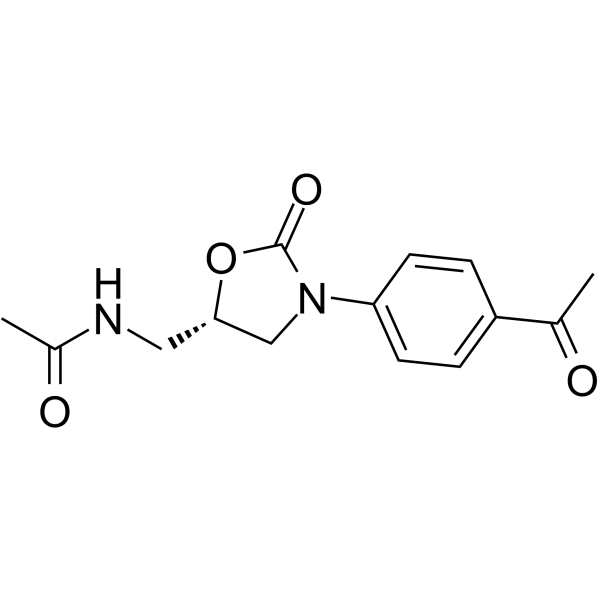
| SMILES | C(C1C=CC(N2CC(CNC(=O)C)OC2=O)=CC=1)(=O)C |
| InChi Key | POXUJOYUVLWPQN-ZDUSSCGKSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C14H16N2O4/c1-9(17)11-3-5-12(6-4-11)16-8-13(20-14(16)19)7-15-10(2)18/h3-6,13H,7-8H2,1-2H3,(H,15,18)/t13-/m0/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (S)-N-((3-(4-acetylphenyl)-2-oxooxazolidin-5-yl)methyl)acetamide |
| Synonyms | Dup-721; Dup721; Dup 721; |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | DuP-721 (1.5-4 μg/ml) suppresses Mycobacterium TB strains that are both susceptible to and resistant to traditional antituberculosis medications. Furthermore, it exhibits no cross resistance to any of the studied anti-tuberculosis medications[1]. At 250 μg/ml, DuP-721 is ineffective against M. avium and M. intracellulare. M. kansassi and M. scrofulaceum are inhibited at 1.95 μg/ml and 15.6 μg/ml, respectively, and M. gordonoe and M. fortuitum at 3.9 μg/ml[1]. |
| ln Vivo | Oral gavage of DuP-721 (50-160 mg/kg) provides protection against M. mouse infection with TB. When given daily for 17 days at a dose of 50 mg/kg po, DuP-721 completely protects all infected animals. When the drug is only given on days 11 and 12, post-infection, the same result is seen at a dose of 160 mg/kg[1]. |
| References | [1]. Affiliatio, et al. Antimycobacterial activities of oxazolidinones: a review. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2006 Dec;6(4):343-54. |
| Additional Infomation | See also: 4-Acetylphenyloxooxazolidinylmethylacetamide (annotation moved to). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (361.94 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.05 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.05 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.05 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.6194 mL | 18.0969 mL | 36.1939 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7239 mL | 3.6194 mL | 7.2388 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3619 mL | 1.8097 mL | 3.6194 mL |