Dimethylcurcumin (formerly known as ASC-J9; GO-Y025) is an androgen receptor (AR) degradation enhancer that effectively suppresses castration resistant prostate cancer cell proliferation and invasion. Dimethylcurcumin suppresses renal cell carcinoma progression by targeting an androgen receptor-dependent HIF2α/VEGF signaling pathway.ASC-J9 treatment enhanced BCG efficacy to suppress bladder cancer cell proliferation via increasing the recruitment of monocytes/macrophages that involved the promotion of BCG attachment/internalization to the bladder cancer cells through increased integrin-α5β1 expression and IL6 release.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C23H24O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 396.43306 |
| Exact Mass | 396.157 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 69.68; H, 6.10; O, 24.21 |
| CAS # | 52328-98-0 |
| Appearance | Light yellow to red solid powder |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 588.6±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 129-130 °C |
| Flash Point | 201.8±23.6 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.608 |
| LogP | 4.05 |
| SMILES | O=C(/C=C(O)/C=C/C1=CC=C(OC)C(OC)=C1)/C=C/C2=CC=C(OC)C(OC)=C2 |
| InChi Key | ZMGUKFHHNQMKJI-CIOHCNBKSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C23H24O6/c1-26-20-11-7-16(13-22(20)28-3)5-9-18(24)15-19(25)10-6-17-8-12-21(27-2)23(14-17)29-4/h5-15,24H,1-4H3/b9-5+,10-6+,18-15- |
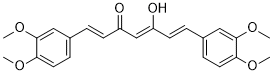
| Chemical Name | (1E,4Z,6E)-1,7-bis(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-5-hydroxyhepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one |
| Synonyms | ASC-J9; ASC-J-9; ASC J9; GO-Y025; GO-Y 025; GO Y025; |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | androgen receptor (AR) degradation enhancer |
| ln Vitro | In a range of human PCa cells, dimethylcurcumin (ASC-J9) can degrade fAR and AR3 in a dose-dependent manner. In CWR22Rv1-fARKD cells, dimethylcurcumin (ASC-J9) can also efficiently block genes that are targeted by AR. In all three PCa cell lines, dimethylcurcumin (ASC-J9) (5 or 10 µM) effectively reduced DHT-induced cell proliferation. Dimethylcurcumin (ASC-J9) breaks down fAR and ectopic AR3 in C81 and C4-2 cells, which suppresses the development of cells and genes targeted by AR [1]. Dimethylcurcumin (ASC-J9) breaks off the connection between AR and AR coregulators, hence preferentially promoting the degradation of AR. Cells accumulate less AR when ASC-J9 AR-112Q is present. SBMA PC12/AR-112Q cell aggregation of AR-112Q is inhibited by dimethylcurcumin (ASC-J9) [2]. |
| ln Vivo | In xenograft tumors, dimethylcurcumin (ASC-J9) (75 mg/kg, i.p.) degrades fAR and AR3, and tumors treated with SC-J9 exhibit a significant reduction in Ki67-positive cells [1]. In AR-97Q mice, intraperitoneal injections of 50 mg/kg dimethylcurcumin (ASC-J9) every 48 hours markedly reduced the symptoms of SBMA and enhanced neuromuscular pathology. Serum testosterone concentrations in SBMA animals treated with dimethylcurcumin (ASC-J9) are comparatively normal [2]. When compared to mice getting traditional ADT/castration with low serum androgen levels, mice treated with ASC-J9 showed noticeably reduced prostate tumor sizes [3]. |
| Enzyme Assay |
Western Blot Analysis, Quantitative Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction, and Luciferase Reporter Assay [1] Cells were cultured and treated with or without ASC-J9 for 24 hours in 10% charcoal-dextran-stripped fetal bovine serum (CD-FBS) media. Cell lysates were harvested and subjected to Western blot analysis. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) was performed in triplicate with a Bio-Rad iCycler system (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA); and messenger RNA (mRNA) levels of PSA, TMPRSS2, FKBP5, and GAPDH were measured. Cells were transiently transfected with mouse mammary tumor virus luciferase reporter (MMTV-Luc) or ARE4-Luc plus pRL-TK as internal control. Luciferase activities were measured using GloMax 20/20 Luminometer (Promega, Madison, WI). |
| Cell Assay |
Cell Growth Assay[1] Cells were treated with vehicle, 1 nM dihydrotestosterone (DHT), 5 µM Casodex, and 5 or 10 µM ASC-J9 in 10% CD-FBS medium. The media were replenished every other day, and we followed the standard MTT assay protocol. |
| Animal Protocol |
In Vivo Tumor Growth Assay [1] Animal procedures were conducted in accordance with the protocol approved by the University of Rochester Committee on Animal Resources. CWR22Rv1 cells (1 x 106 cells per site) were injected into both anterior prostates (orthotopic) of castrated nude mouse after 2 weeks of implantation. The mice were randomly divided into two groups (four mice/eight tumors each group) and either received 75 mg/kg ASC-J9 intraperitoneal injection or vehicle control every other day. After 4 weeks of treatment, all mice were killed to examine the tumor growth. Body weights and mice activity were measured weekly. |
| References |
[1]. ASC-J9 suppresses castration-resistant prostate cancer growth through degradation of full-length and splice variant androgen receptors. Neoplasia. 2012 Jan;14(1):74-83. [2]. ASC-J9 ameliorates spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy phenotype via degradation of androgen receptor. Nat Med. 2007 Mar;13(3):348-53. [3]. New therapy targeting differential androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer stem/progenitor vs non-stem/progenitor cells. J Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Jul 24. [4]. Targeting androgen receptor with ASC-J9 attenuates cardiac injury and dysfunction in experimental autoimmune myocarditis by reducing M1-like macrophage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Apr 15;485(4):746-752. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.02.123. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : ≥ 50 mg/mL (~126.13 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.17 mg/mL (5.47 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 21.7 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.2 mg/mL (5.5 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + + 45% Saline For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL of 21.7 mg/mL of DMSO stock solution and add tO + 400 μL of PEG300, mix well (clear solution); Then add 50 μL of Tween 80 to the above solution, mix well (clear solution); Finally, add 450 μL of saline to the above solution, mix well (clear solution). Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in ddH ₂ O and make up to 100 mL to obtain a clear and transparent saline solution. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5225 mL | 12.6126 mL | 25.2251 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5045 mL | 2.5225 mL | 5.0450 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2523 mL | 1.2613 mL | 2.5225 mL |