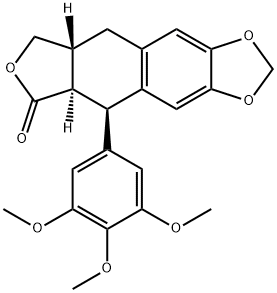
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C22H22O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 398.4059 |
| Exact Mass | 398.136 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 66.32; H, 5.57; O, 28.11 |
| CAS # | 19186-35-7 |
| Related CAS # | 19186-35-7 |
| PubChem CID | 345501 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 564.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 247.0±30.2 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.587 |
| LogP | 2.44 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 29 |
| Complexity | 598 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| SMILES | O1C([C@]2([H])[C@]([H])(C3C([H])=C(C(=C(C=3[H])OC([H])([H])[H])OC([H])([H])[H])OC([H])([H])[H])C3=C([H])C4=C(C([H])=C3C([H])([H])[C@@]2([H])C1([H])[H])OC([H])([H])O4)=O |
| InChi Key | ZGLXUQQMLLIKAN-SVIJTADQSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C22H22O7/c1-24-17-6-12(7-18(25-2)21(17)26-3)19-14-8-16-15(28-10-29-16)5-11(14)4-13-9-27-22(23)20(13)19/h5-8,13,19-20H,4,9-10H2,1-3H3/t13-,19+,20-/m0/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (5R,5aR,8aR)-5-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-5a,8,8a,9-tetrahydro-5H-[2]benzofuro[5,6-f][1,3]benzodioxol-6-one |
| Synonyms | Deoxypodophyllotoxin; Anthricin; AS2-3; AS 2-3; AS-2-3 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | Deoxypodophyllotoxin (25-75 nM; 6-48 hours) increases, for 24 and 48 hours, the proportion of early apoptotic cell population from 2.05 to 5.62 and 18.49%, respectively[1]. Deoxypodophyllotoxin (25-75 nM; 6-48 hours) treats G2/M-arrested SGC-7901 cells in a time- and dose-dependent manner[1]. Deoxypodophyllotoxin (25–75 nM; 6-48 hours) significantly reduces the expression levels of Cdc2 and Cdc25C in a time- and dose-dependent manner, increases cyclin B1 within 6 hours, and lowers the activity of PARP, Bcl-2, and caspase-3[1]. |
| ln Vivo | Deoxypodophyllotoxin (intravenously injected; 5, 10, and 20 mg/kg; 3 times a week; 28 days) suppresses tumors in a dose-dependent manner; at 5, 10, and 20 mg/kg, DPT inhibits tumor growth by 22.19%, 47.91%, and 50.93%, respectively[1]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Xenograft model of gastric cancer in nude mice with SGC-7901 cells[1] 5, 10, and 20 mg/kg Intravenously injected; 5, 10, and 20 mg/kg; 3 times a week; 28 days |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Metabolism / Metabolites Deoxypodophyllotoxin has known human metabolites that include 5-(4-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-5a,8,8a,9-tetrahydro-5H-[2]benzofuro[5,6-f][1,3]benzodioxol-6-one, 6,7-Dihydroxy-4-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-3a,4,9,9a-tetrahydro-1H-benzo[f][2]benzofuran-3-one, and 5-hydroxy-9-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-5a,6,8a,9-tetrahydro-5H-[2]benzofuro[5,6-f][1,3]benzodioxol-8-one. |
| References |
[1]. Deoxypodophyllotoxin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in SGC-7901 cells and inhibits tumor growth in vivo. Molecules. 2015 Jan 20;20(1):1661-75. [2]. Deoxypodophyllotoxin induces cytoprotective autophagy against apoptosis via inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in osteosarcoma U2OS cells. Pharmacol Rep. 2017 Oct;69(5):878-884. [3]. Pharmacological effect of deoxypodophyllotoxin: a medicinal agent of plant origin, on mammalian neurons. Neurotoxicology. 2010 Dec;31(6):680-6. |
| Additional Infomation |
Deoxypodophyllotoxin is a member of the class of furonaphthodioxoles that is (5R,5aR,8aR)-5,8,8a,9-tetrahydro-2H-furo[3',4':6,7]naphtho[2,3-d][1,3]dioxol-6(5aH)-one substituted at position 5 by a 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl group. It has a role as a plant metabolite, an antineoplastic agent and an apoptosis inducer. It is a lignan, a furonaphthodioxole, a gamma-lactone and a member of methoxybenzenes. Deoxypodophyllotoxin has been reported in Dysosma aurantiocaulis, Dysosma pleiantha, and other organisms with data available. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO: ~80 mg/mL (~200.8 mM) Ethanol: ~10 mg/mL (~25.1 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.27 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.27 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.27 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5100 mL | 12.5499 mL | 25.0998 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5020 mL | 2.5100 mL | 5.0200 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2510 mL | 1.2550 mL | 2.5100 mL |