Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C72H79FN10O17 |
| Molecular Weight | 1375.45 |
| Exact Mass | 1374.56 |
| CAS # | 2694856-51-2 |
| PubChem CID | 162642643 |
| Appearance | Off-white to light yellow solid powder |
| Density | 1.43±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| LogP | 0.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 19 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 34 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 100 |
| Complexity | 3060 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
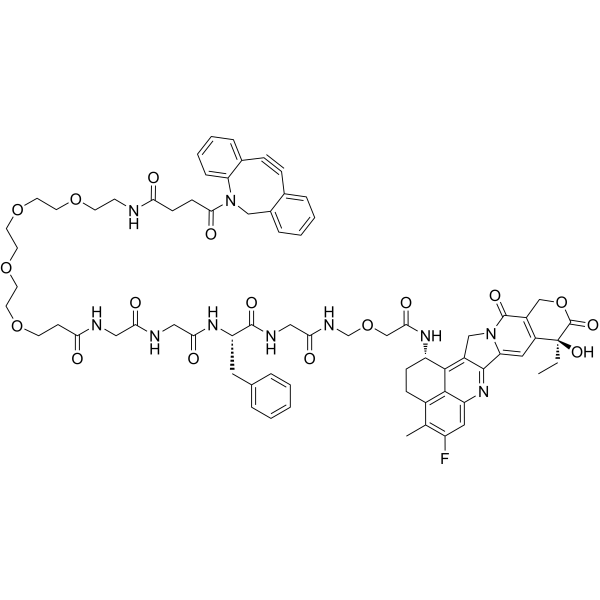
| SMILES | FC1=CC2=C3C(=C1C)CC[C@@H](C3=C1C(C3=CC4[C@](C(=O)OCC=4C(N3C1)=O)(CC)O)=N2)NC(COCNC(CNC([C@H](CC1C=CC=CC=1)NC(CNC(CNC(CCOCCOCCOCCOCCNC(CCC(N1C2C=CC=CC=2C#CC2C=CC=CC=2C1)=O)=O)=O)=O)=O)=O)=O)=O |
| InChi Key | UCUZJQMJKLKGGT-OHZCADGZSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C72H79FN10O17/c1-3-72(94)52-34-58-68-50(40-83(58)70(92)51(52)41-100-71(72)93)67-54(20-19-49-44(2)53(73)35-55(81-68)66(49)67)79-64(89)42-99-43-78-62(87)37-77-69(91)56(33-45-11-5-4-6-12-45)80-63(88)38-76-61(86)36-75-60(85)23-25-95-27-29-97-31-32-98-30-28-96-26-24-74-59(84)21-22-65(90)82-39-48-15-8-7-13-46(48)17-18-47-14-9-10-16-57(47)82/h4-16,34-35,54,56,94H,3,19-33,36-43H2,1-2H3,(H,74,84)(H,75,85)(H,76,86)(H,77,91)(H,78,87)(H,79,89)(H,80,88)/t54-,56-,72-/m0/s1 |
| Chemical Name | 4-(2-azatricyclo[10.4.0.04,9]hexadeca-1(16),4,6,8,12,14-hexaen-10-yn-2-yl)-N-[2-[2-[2-[2-[3-[[2-[[2-[[(2S)-1-[[2-[[2-[[(10S,23S)-10-ethyl-18-fluoro-10-hydroxy-19-methyl-5,9-dioxo-8-oxa-4,15-diazahexacyclo[14.7.1.02,14.04,13.06,11.020,24]tetracosa-1,6(11),12,14,16,18,20(24)-heptaen-23-yl]amino]-2-oxoethoxy]methylamino]-2-oxoethyl]amino]-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]amino]-3-oxopropoxy]ethoxy]ethoxy]ethoxy]ethyl]-4-oxobutanamide |
| Synonyms | DBCO-PEG4-GGFG-Exatecan; DBCO-PEG4-GGFG-DX8951; 2694856-51-2; DBCO-PEG4-GGFG-Dxd; 7L3XY83XWU; |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: This product requires protection from light (avoid light exposure) during transportation and storage. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Traditional Cytotoxic Agents |
| ln Vitro | ADCs are made up of an antibody and an ADC cytotoxin that are joined together by an ADC link[1]. |
| References |
[1]. Antibody-drug conjugates for cancer therapy. Lancet Oncol. 2016 Jun;17(6):e254-e262. |
| Additional Infomation | Antibody-drug conjugates are monoclonal antibodies conjugated to cytotoxic agents. They use antibodies that are specific to tumour cell-surface proteins and, thus, have tumour specificity and potency not achievable with traditional drugs. Design of effective antibody-drug conjugates for cancer therapy requires selection of an appropriate target, a monoclonal antibody against the target, potent cytotoxic effector molecules, and conjugation of the monoclonal antibody to cytotoxic agents. Substantial advances in all these aspects in the past decade have resulted in regulatory approval of ado-trastuzumab emtansine and brentuximab vedotin for clinical use. Several promising antibody-drug conjugates are now in late-phase clinical testing. Ongoing efforts are focused on identifying better targets, more effective cytotoxic payloads, and further improvements in antibody-drug linker technology. Improved understanding of the mechanistic basis of antibody-drug conjugate activity will enable design of rational combination therapies with other agents, including immunotherapy. [1] |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : 50 mg/mL (36.35 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (1.82 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: 2.5 mg/mL (1.82 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: 2.5 mg/mL (1.82 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.7270 mL | 3.6352 mL | 7.2703 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.1454 mL | 0.7270 mL | 1.4541 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.0727 mL | 0.3635 mL | 0.7270 mL |