Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C52H83N7O13S |
| Molecular Weight | 1046.3195335865 |
| Exact Mass | 1045.576 |
| CAS # | 1160590-05-5 |
| Related CAS # | 1160590-05-5 |
| PubChem CID | 86278355 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| LogP | 1.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 15 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 31 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 73 |
| Complexity | 1880 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 10 |
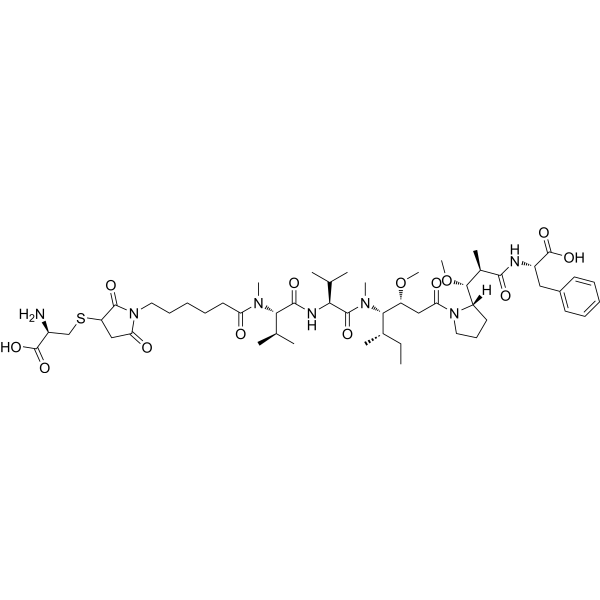
| SMILES | S(C[C@@H](C(=O)O)N)C1C(N(C(C1)=O)CCCCCC(N(C)[C@@H](C(C)C)C(N[C@@H](C(C)C)C(N(C)[C@@H]([C@@H](C)CC)[C@@H](CC(N1CCC[C@H]1[C@@H]([C@H](C(N[C@H](C(=O)O)CC1C=CC=CC=1)=O)C)OC)=O)OC)=O)=O)=O)=O |
| InChi Key | BXTJCSYMGFJEID-XMTADJHZSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C52H83N7O13S/c1-12-32(6)45(38(71-10)27-41(61)58-25-19-22-37(58)46(72-11)33(7)47(63)54-36(52(69)70)26-34-20-15-13-16-21-34)57(9)50(66)43(30(2)3)55-48(64)44(31(4)5)56(8)40(60)23-17-14-18-24-59-42(62)28-39(49(59)65)73-29-35(53)51(67)68/h13,15-16,20-21,30-33,35-39,43-46H,12,14,17-19,22-29,53H2,1-11H3,(H,54,63)(H,55,64)(H,67,68)(H,69,70)/t32-,33+,35-,36-,37-,38+,39?,43-,44-,45-,46+/m0/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (2S)-2-[[(2R,3R)-3-[(2S)-1-[(3R,4S,5S)-4-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[6-[3-[(2R)-2-amino-2-carboxyethyl]sulfanyl-2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl]hexanoyl-methylamino]-3-methylbutanoyl]amino]-3-methylbutanoyl]-methylamino]-3-methoxy-5-methylheptanoyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl]-3-methoxy-2-methylpropanoyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoic acid |
| Synonyms | Cys-McMMAF |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: This product requires protection from light (avoid light exposure) during transportation and storage. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vivo | Cys-McMMAF (0.3 mg/kg, 3 mg/kg; intravenous injection; single dosage) shows moderate stability in cynomolgus monkeys with a short base time [1]. Pharmacokinetic study in nude mice (nu/nu) [1] Model/IV dose (mg/kg) Cmax (ng/mL) Tmax (hr) AUC0-336 (ng·h/mL) t1/2 (day) Non-tumor 1 0.192 8 14.6 2.1 Tumor 1 0.146 8 28.2 6.0 Non-tumor 10 0.951 8 58.5 3.0 Tumor 10 0.945 8 81.9/td> 2.9 |
| References |
[1]. Preclinical Development of an anti-5T4 Antibody-Drug Conjugate: Pharmacokinetics in Mice, Rats, and NHP and Tumor/Tissue Distribution in Mice. Bioconjug Chem. 2015 Nov 18;26(11):2223-32. |
| Additional Infomation |
Depatuxizumab/Denintuzumab mafodotin has been used in trials studying the treatment of Lymphoma, Gliosarcoma, Glioblastoma, Malignant Glioma, Squamous Cell Tumors, and Glioblastoma Multiforme. Vorsetuzumab mafodotin is under investigation in clinical trial NCT01677390 (A Phase 1b Study of SGN-75 in Combination With Everolimus in Patients With Renal Cell Carcinoma). Denintuzumab Mafodotin is an immunoconjugate consisting of an anti-CD19 monoclonal antibody conjugated to the auristatin derivative monomethyl auristatin F (MMAF), with potential antineoplastic activity. Upon administration of denintuzumab mafodotin, the antibody moiety targets the cell surface antigen CD19, found on a number of B-cell-derived cancers. Upon antibody/antigen binding and internalization, the immunoconjugate releases MMAF, which binds to tubulin and inhibits its polymerization. Inhibition of tubulin polymerization may result in G2/M phase arrest and tumor cell apoptosis. This causes inhibition of cell growth of CD19-expressing tumor cells. CD19, a B-cell antigen, is overexpressed by a variety of different cancer cell types. Depatuxizumab Mafodotin is an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitor, with potential antineoplastic activity. Upon intravenous infusion, depatuxizumab mafodotin inhibits the activity of EGFR, thereby preventing EGFR-mediated signaling. This may inhibit tumor growth in EGFR-overexpressing tumor cells. EGFR, a receptor tyrosine kinase overexpressed in certain tumor cell types, plays a key role in tumor cell proliferation and tumor vascularization. Vorsetzumab Mafodotin is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) consisting of a humanized monoclonal antibody, directed against the extracellular domain of the human CD70 molecule, conjugated to the auristatin analogue monomethyl auristatin phenylalanine (MMAF), with potential antineoplastic activity. The anti-CD70 antibody moiety of vorsetuzumab mafodotin selectively binds to the extracellular domain of CD70 on tumor cell surfaces. Upon internalization, the MMAF moiety is released, binds to tubulin and inhibits its polymerization, which may result in G2/M phase arrest, tumor cell apoptosis and inhibition of cellular proliferation in tumor cells that overexpress CD70. CD70, the ligand for the costimulatory receptor CD27 and a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family, is found on the surfaces of various types of cancer cells. Drug Indication No approved indication. Mechanism of Action Depatuxizumab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody for EGFR which is linked to monomethyl aurastatin F via a maleimidocaproyl linker (mafodotin). Once delivered to the cancer cell, the mafodotin component is able to bind to tubulin and inhibit the exchange of GDP for GTP necessary for the polymerization of tubulin subunits to form microtubules. The inhibition of microtubule polymerization disrupts mitosis and interferes with vesicle trafficking in the cancer cell. Pharmacodynamics Selectively targets cancer cells expressing mutant epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) vIII or over expressing wild type EGFR. Depatuxizumab mafodotin acts on these cells to inhibit microtuble polymerization thus disrupting mitosis and vesicular trafficking |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: ~200 mg/mL (~191.2 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 5 mg/mL (4.78 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 50.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: 5 mg/mL (4.78 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 50.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 5 mg/mL (4.78 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 50.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.9557 mL | 4.7787 mL | 9.5573 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.1911 mL | 0.9557 mL | 1.9115 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.0956 mL | 0.4779 mL | 0.9557 mL |