Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C16H12O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 300.26 |
| Exact Mass | 300.063 |
| CAS # | 491-71-4 |
| PubChem CID | 5280666 |
| Appearance | Light yellow to yellow solid powder |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 574.3±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | >300ºC (dec.) |
| Flash Point | 219.4±23.6 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.697 |
| LogP | 1.81 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Complexity | 462 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| InChi Key | SCZVLDHREVKTSH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C16H12O6/c1-21-14-4-8(2-3-10(14)18)13-7-12(20)16-11(19)5-9(17)6-15(16)22-13/h2-7,17-19H,1H3 |
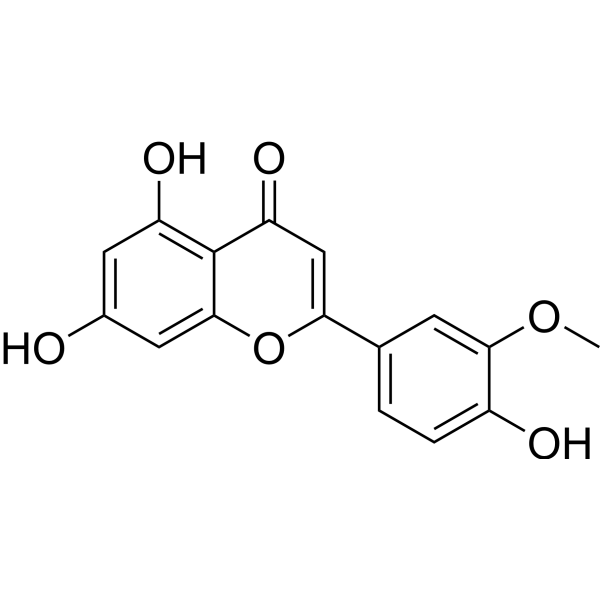
| Chemical Name | 5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)chromen-4-one |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: This product requires protection from light (avoid light exposure) during transportation and storage. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Metabolism / Metabolites Chrysoeriol has known human metabolites that include (2S,3S,4S,5R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-[5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxochromen-7-yl]oxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid. |
| References |
[1]. Effect of O-glycosilation on the Antioxidant Activity and Free Radical Reactions of a Plant Flavonoid, Chrysoeriol. Bioorg Med Chem. 2003 Jul 3;11(13):2677-85. |
| Additional Infomation |
4',5,7-trihydroxy-3'-methoxyflavone is the 3'-O-methyl derivative of luteolin. It has a role as an antineoplastic agent, an antioxidant and a metabolite. It is a trihydroxyflavone and a monomethoxyflavone. It is functionally related to a luteolin. It is a conjugate acid of a 4',5-dihydroxy-3'-methoxyflavon-7-olate(1-). Chrysoeriol has been reported in Schouwia thebaica, Perilla frutescens, and other organisms with data available. See also: Acai (part of); Acai fruit pulp (part of). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO :~100 mg/mL (~333.04 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.33 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: 2.5 mg/mL (8.33 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.33 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3304 mL | 16.6522 mL | 33.3045 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6661 mL | 3.3304 mL | 6.6609 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3330 mL | 1.6652 mL | 3.3304 mL |