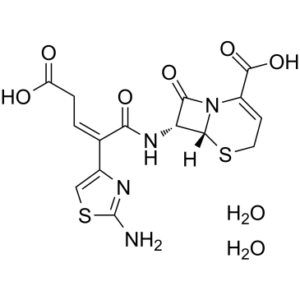
Ceftibuten dihydrate, a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic, is the dihydrate form of ceftibuten which is a semisynthetic, beta-lactamase-stable, cephalosporin with antibacterial activity. Ceftibuten inactivates penicillin-binding proteins located on the inner membrane of the bacterial cell wall. This results in the weakening of the bacterial cell wall and causes cell lysis.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C15H18N4O8S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 446.4554 |
| Exact Mass | 446.056 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 40.35; H, 4.06; N, 12.55; O, 28.67; S, 14.36 |
| CAS # | 118081-34-8 |
| Related CAS # | Ceftibuten;97519-39-6;Ceftibuten hydrate;1346153-47-6 |
| PubChem CID | 5282241 |
| Appearance | Light yellow to yellow solid powder |
| Boiling Point | 966.4ºC at 760mmHg |
| Melting Point | >180ºC (dec.) |
| Flash Point | 538.3ºC |
| Vapour Pressure | 0mmHg at 25°C |
| LogP | 0.733 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 12 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 29 |
| Complexity | 755 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| SMILES | S1C([H])([H])C([H])=C(C(=O)O[H])N2C([C@]([H])([C@@]12[H])N([H])C(/C(=C(/[H])\C([H])([H])C(=O)O[H])/C1=C([H])SC(N([H])[H])=N1)=O)=O.O([H])[H].O([H])[H] |
| InChi Key | SSWTVBYDDFPFAF-ODPSPGRDSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C15H14N4O6S2.2H2O/c16-15-17-7(5-27-15)6(1-2-9(20)21)11(22)18-10-12(23)19-8(14(24)25)3-4-26-13(10)19;;/h1,3,5,10,13H,2,4H2,(H2,16,17)(H,18,22)(H,20,21)(H,24,25);2*1H2/b6-1+;; |
| Chemical Name | (6R,7R)-7-[[(Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-4-carboxybut-2-enoyl]amino]-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid;dihydrate |
| Synonyms | Sch 39720 dihydrate; Sch-39720 dihydrate; Sch39720 dihydrate; Ceftibuten Dihydrate; UNII-62F4443RWP; Seftem; ceftibuten.2H2O; Seftem (TN); Cedax (TN); AC1NQZPM; SCHEMBL159144; CHEBI:34618; HY-B0698A; 62F4443RWP; AKOS025149353; AN-6406; HE068843; HE299817; O441; FT-0664440; D02121; A803878; I06-1263 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | β-lactam |
| ln Vitro | Ceftibuten (Sch-39720) exhibits moderate activity against Serratia sp.and Streptococcus pyogenes, but is highly active against Haemophilus influenza, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella sp., and Proteus sp. Ceftibuten only exhibits weak activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and obligate anaerobes, and it is comparatively inactive against enterococci and staphylococci. With the exception of Bacteroides fragilis, it remains stable when most β-lactamase-producing organisms are present. Ceftibuten exhibits high potency against Enterobacteriaceae strains (mean MIC for 90% of strains = 0.25 μg/ml); however, it has comparatively lower efficacy against Campylobacter jejuni strains (mean MIC for 90% of strains = 16.0 μg/ml)[1]. |
| ln Vivo | Ceftibuten is a biologically stable β-lactam antibiotic that has been demonstrated to exhibit distinct stereoselective and proton-gradient dependent transport characteristics in rat intestinal brush-border membrane vesicles. It has also been shown to be transported by the small peptide transport system and to have a relatively high affinity for the carrier[3]. |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Limited information indicates that ceftibuten produces low levels in milk that are not expected to cause adverse effects in breastfed infants. Occasionally disruption of the infant's gastrointestinal flora, resulting in diarrhea or thrush have been reported with cephalosporins, but these effects have not been adequately evaluated. Ceftibuten is acceptable in nursing mothers. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. |
| References |
[1]. Single-dose pharmacokinetics of ceftibuten (SCH 39720) in infants and children. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991;35(10):2078-2084. [2]. Comparative in vitro activity of ceftibuten (Sch 39720) against bacterial enteropathogens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989;33(5):781-784. [3]. Functional expression of intestinal dipeptide/beta-lactam antibiotic transporter in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1994;48(5):881-888. [4]. J Antimicrob Chemother, 1990. 26(2): p. 209-213. |
| Additional Infomation |
Ceftibuten dihydrate is the dihydrate of ceftibuten. It is used as an orally administered treatment for urinary-tract and respiratory-tract infections. It has a role as an antibacterial drug. It contains a ceftibuten. Ceftibuten Dihydrate is the dihydrate form of ceftibuten, a semisynthetic, beta-lactamase-stable, third-generation cephalosporin with antibacterial activity. Ceftibuten binds to and inactivates penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located on the inner membrane of the bacterial cell wall. PBPs are enzymes involved in the terminal stages of assembling the bacterial cell wall and in reshaping the cell wall during growth and division. Inactivation of PBPs interferes with the cross-linkage of peptidoglycan chains necessary for bacterial cell wall strength and rigidity. This results in the weakening of the bacterial cell wall and causes cell lysis. A cephalosporin antibacterial agent that is used in the treatment of infections, including urinary-tract and respiratory-tract infections. See also: Ceftibuten (has active moiety). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
H2O : ~100 mg/mL (~223.98 mM) DMSO : 90~100 mg/mL (201.58~223.98 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.60 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.60 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.60 mM) Solubility in Formulation 4: 2.26 mg/mL (5.06 mM) in PBS (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with ultrasonication. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2398 mL | 11.1992 mL | 22.3984 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4480 mL | 2.2398 mL | 4.4797 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2240 mL | 1.1199 mL | 2.2398 mL |