Caerulomycin A (also known as Cerulomycin, CaeA) is a novel bipyridyl compound that induces generation of T cells, enhances TGF-β-Smad3 protein signaling via suppressing interferon-γ-induced STAT1 signaling. It is also a toxin that inhibits growth of Entamoeba. It has antifungal and antibiotic activity, and can be used in autoimmune diseases. Cytokines play a very important role in the regulation of immune homeostasis. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) responsible for the generation of peripheral tolerance are under the tight regulation of the cytokine milieu. It was observed that Caerulomycin A substantially up-regulated the pool of Tregs, as evidenced by an increased frequency of CD4(+) Foxp3(+) cells. In addition, CaeA significantly suppressed the number of Th1 and Th17 cells, as supported by a decreased percentage of CD4(+)/IFN-γ(+) and CD4(+)/IL-17(+) cells, respectively.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C12H11N3O2 | |
| Molecular Weight | 229.23 | |
| Exact Mass | 229.085 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 62.87; H, 4.84; N, 18.33; O, 13.96 | |
| CAS # | 21802-37-9 | |
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID | 135514797 | |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder | |
| Density | 1.23g/cm3 | |
| Boiling Point | 400.4ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Flash Point | 195.9ºC | |
| LogP | 1.96 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 17 | |
| Complexity | 260 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 | |
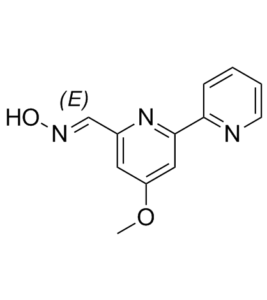
| SMILES | COC1=CC(C2=NC=CC=C2)=NC(/C=N/O)=C1 |
|
| InChi Key | JCTRJRHLGOKMCF-RIYZIHGNSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C12H11N3O2/c1-17-10-6-9(8-14-16)15-12(7-10)11-4-2-3-5-13-11/h2-8,16H,1H3/b14-8+ | |
| Chemical Name | (E)-4-methoxy-[2,2'-bipyridine]-6-carbaldehyde oxime | |
| Synonyms | Carulomycin A; AC1NTHG8; AC1N-THG8; AC1N THG8 NSC-114341; NSC114341; NSC 114341; HE185727; HE 185727; HE-185727; Caerulomycin A | |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Antifungal;TGF-β-Smad3 |
| ln Vitro | Caerulomycin A (CaeA), in inducing the generation of Tregs. It was observed that CaeA substantially up-regulated the pool of Tregs, as evidenced by an increased frequency of CD4(+) Foxp3(+) cells. In addition, CaeA significantly suppressed the number of Th1 and Th17 cells, as supported by a decreased percentage of CD4(+)/IFN-γ(+) and CD4(+)/IL-17(+) cells, respectively. Furthermore, we established the mechanism and observed that CaeA interfered with IFN-γ-induced STAT1 signaling by augmenting SOCS1 expression. An increase in the TGF-β-mediated Smad3 activity was also noted. Furthermore, CaeA rescued Tregs from IFN-γ-induced inhibition. These results were corroborated by blocking Smad3 activity, which abolished the CaeA-facilitated generation of Tregs. In essence, our results indicate a novel role of CaeA in inducing the generation of Tregs. This finding suggests that CaeA has enough potential to be considered as a potent future drug for the treatment of autoimmunity.[1] |
| Cell Assay |
Th1 and Th17 cells were treated with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (40 nm) and ionomycin (1 μm) for 2 h. To block cytokine secretion, brefeldin A (10 μg/ml) was added. Later, and cells were incubated further for 3 h. Tregs, Th1, and Th17 cells were cultured with different concentrations of CaeA (0–0.15 μm). The modulation in the frequency of Tregs, Th1, and Th17 cells was analyzed by flow cytometry.[1] A booster dose of bovine collagen type II in incomplete Freund adjuvant was injected on day 21. Later, CaeA (1 and 10 mg/kg body weight) and 0.5% carboxyl methyl cellulose emulsion in water was administered daily for 50 days, and animals were monitored every day for arthritis symptoms. [1] The IFN-γ-mediated STAT1 response was measured by initially incubating CD4 T cells with CaeA (0–0.31 μm) for 24 h, followed by IFN-γ (200 units/ml) stimulation for 30 min. To evaluate the TGF-β-mediated Smad3 response, CD4 T cells were incubated initially with CaeA (0–0.31 μm) for 24 h, followed by IFN-γ (200 units/ml) treatment for 48 h. Later, cells were pulsed with TGF-β (2 ng/ml) for 1 h. [1] CD4 T cells stimulated with anti-CD3 (2 μg/ml) and CD28 (1 μg/ml) Abs were cultured with CaeA (0–0.31 μm) for 72 h. Later, cells were pelleted and resuspended in JC-1 (5,5′,6,6′-tetrachloro-1,1′,3,3′-tetraethylbenzimidazolylcarbocyanine iodide) medium (2.5 μg/ml). The cultures were incubated at room temperature for 15–20 min in the dark. Later, cells were washed with flow cytometry staining buffer (2% FBS in PBS) and acquired immediately using a flow cytometer (FACSCalibur), and then the analysis was done using FACSDiva software. [1] |
| References |
[1]. Caerulomycin A enhances transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)-Smad3 protein signaling by suppressing interferon-γ (IFN-γ)-signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) protein signaling to expand regulatory T cells (Tregs). J Biol Chem. 2014 Jun 20;289(25):17515-28. |
| Additional Infomation |
Caerulomycin A is a pyridine alkaloid that is 2,2'-bipyridine substituted by a methoxy group at position 4 and a (E)-(hydroxyimino)methyl group at position 6. Isolated from the marine-derived actinomycete Actinoalloteichus cyanogriseus, it exhibits antineoplastic activity. It has a role as an antineoplastic agent, a marine metabolite and a bacterial metabolite. It is an aldoxime, an aromatic ether, a member of bipyridines and a pyridine alkaloid. It derives from a hydride of a 2,2'-bipyridine. Cerulomycin has been reported in Actinoalloteichus cyanogriseus with data available. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : ~150 mg/mL (~654.34 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (10.91 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (10.91 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (10.91 mM) (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.3624 mL | 21.8122 mL | 43.6243 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.8725 mL | 4.3624 mL | 8.7249 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4362 mL | 2.1812 mL | 4.3624 mL |