Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C14H15CL2N3S |
| Molecular Weight | 328.26 |
| Exact Mass | 327.036 |
| CAS # | 2108899-91-6 |
| Related CAS # | CPTH2;357649-93-5 |
| PubChem CID | 129241190 |
| Appearance | Typically exists as solid at room temperature |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 20 |
| Complexity | 321 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| InChi Key | ODVWZAKKCNHATB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C14H14ClN3S.ClH/c15-11-7-5-10(6-8-11)13-9-19-14(16-13)18-17-12-3-1-2-4-12;/h5-9H,1-4H2,(H,16,18);1H |
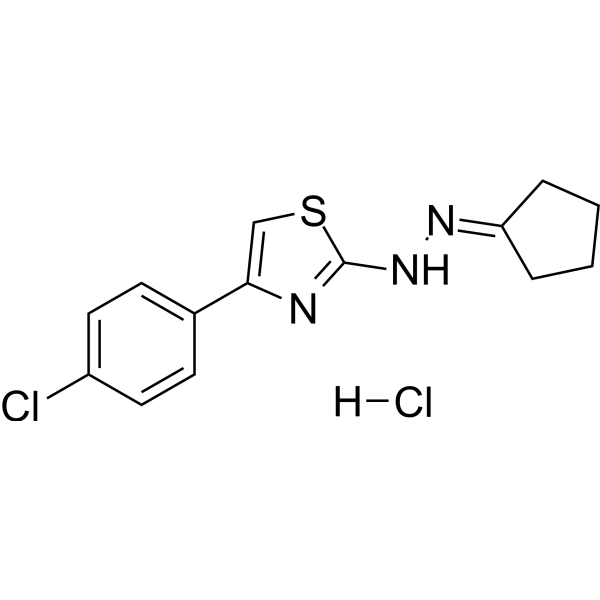
| Chemical Name | 4-(4-chlorophenyl)-N-(cyclopentylideneamino)-1,3-thiazol-2-amine;hydrochloride |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | GCN5 |
| ln Vitro | CPTH2 (100 μM; 12, 24, 48 hours) hydrochloride induces a reduction in cell proliferation that is noticeable as soon as 12 hours after stimulation and even more so after 48 hours[1]. In both cell lines, CPTH2 hydrochloride (100 μM; 12 or 48 hours) results in a similar decrease in activity[1]. After 48 hours, the population of apoptotic/dead cells increases dramatically in response to CPTH2 hydrochloride (100 μM)[1]. Hydrochloride CPTH2 (100 μM; 12, 24, 48 hours) exhibits decreased acetylation of H3AcK18 and the global AcH3 histone[1]. It is possible to prevent the invasion and migration of ccRCC-786-O cells in culture by using CPTH2 hydrochloride (100 μM; 24 48 hours)[1]. (0.2, 0.5, and 1 mM) hydrochloride suppresses the development of a single catalytic mutant E173H and a GCN5 deletion strain[2]. In yeast cell cultures, CPTH2 hydrochloride (0.6, 0.8 mM; for 24 hours) suppresses histone H3 acetylation[2]. The functional network dependent on Gcn5p is inhibited by CPTH2 hydrochloride[2]. |
| Cell Assay |
Cell Proliferation Assay[1] Cell Types: Papillary thyroid (K1) and clear cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (ccRCC-786-O) cell lines Tested Concentrations: 100 μM Incubation Duration: 12, 24, 48 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Caused a decrease in cell proliferation after as early as 12 h with a further significant reduction after 48 h stimulation. Cell Viability Assay[1] Cell Types: K1 and ccRCC-786-O cell lines Tested Concentrations: 100 μM Incubation Duration: 24 hrs (hours) (K1 cell) and 48 hrs (hours) (ccRCC-786-O cell) Experimental Results: Caused a comparable drop of the activity in both cell lines. Apoptosis Analysis[1] Cell Types: ccRCC-786-O cells Tested Concentrations: 100 μM Incubation Duration: 48 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Produced a drastic increase in apoptotic/dead cell population after 48 h. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Types: ccRCC-786-O cells Tested Concentrations: 100 μM Incubation Duration: 12, 24, 48 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: demonstrated a decreased acetylation of both global AcH3 histone and H3AcK18. |
| References |
[1]. KAT3B-p300 and H3AcK18/H3AcK14 levels are prognostic markers for kidney ccRCC tumoraggressiveness and target of KAT inhibitor CPTH2. Clin Epigenetics. 2018 Apr 4;10:44. [2]. A novel histone acetyltransferase inhibitor modulating Gcn5 network: cyclopentylidene-[4-(4'-chlorophenyl)thiazol-2-yl)hydrazone. J Med Chem. 2009 Jan 22;52(2):530-6. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0464 mL | 15.2318 mL | 30.4637 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6093 mL | 3.0464 mL | 6.0927 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3046 mL | 1.5232 mL | 3.0464 mL |