Bay 41-4109 S-isomer is the less active enantiomer of Bay 41-4109. It shows less activity than Bay 41-4109. BAY 41-4109 is a novel and potent inhibitor of human hepatitis B virus (HBV) with an IC50 of 53 nM. BAY-41-4109 is a heteroaryldihydropyrimidine (HAP) antiviral compound effective on Hepatitis B virus (HBV) capsid assembly and on preformed HBV capsids.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C18H13CLF3N3O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 395.7629 |
| Exact Mass | 395.064 |
| CAS # | 476617-51-3 |
| Related CAS # | Bay 41-4109;298708-81-3;Bay 41-4109 racemate;298708-79-9 |
| PubChem CID | 10188768 |
| Appearance | Light yellow to yellow solid powder |
| LogP | 3.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 |
| Complexity | 645 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| SMILES | ClC1C([H])=C(C([H])=C([H])C=1[C@]1([H])C(C(=O)OC([H])([H])[H])=C(C([H])([H])[H])N([H])C(C2=C(C([H])=C(C([H])=N2)F)F)=N1)F |
| InChi Key | FVNJBPMQWSIGJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C18H13ClF3N3O2/c1-8-14(18(26)27-2)15(11-4-3-9(20)5-12(11)19)25-17(24-8)16-13(22)6-10(21)7-23-16/h3-7,15H,1-2H3,(H,24,25) |
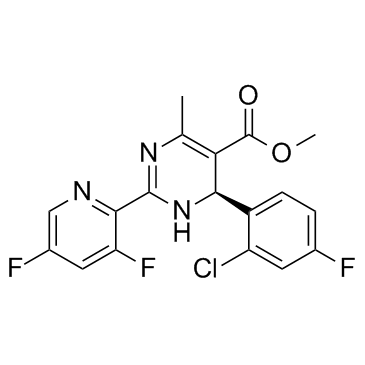
| Chemical Name | (S)-Methyl 4-(2-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-2-(3,5-difluoropyridin-2-yl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidine-5-carboxylate |
| Synonyms | BAY-414109 S-isomer; BAY414109 S-isomer; BAY 414109; BAY-41-4109; BAY41-4109; BAY 41-4109 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | Mice: For this study, HBV-transgenic mice are employed. The compounds (BAY 41-4109) are given to mice twice a day for 28 days in a suspension solution formulated with 0.5% tylose. The placebo is the 0.5% tylose. The animals are killed six hours after the last treatment, and the livers are taken out and frozen right away for further examination. The anesthetized animals' hearts are punctured to obtain blood[1]. |
| ln Vivo | Viral DNA in liver and plasma is dose-dependently reduced by BAY 41-4109, with an efficacy that is similar to that of 3TC. HBV transgenic mice's livers had lower levels of the hepatitis B virus core antigen (HBcAg) when BAY 41 -4109 is added. According to pharmacokinetic studies conducted on mice, rats and dogs exhibit fast absorption, with dose-proportional plasma concentrations of about 60% and a bioavailability of 30% [1]. By focusing on the viral capsid, BAY41-4109 prevents the growth of viruses in vivo [2]. |
| Animal Protocol | Rodents: HBV-transgenic mice are used in this study. For a duration of 28 days, mice are administered the compounds (BAY 41-4109) twice daily in a suspension solution containing 0.5% tylose. 0.5% tylose serves as the placebo. After the animals are killed six hours after the last treatment, the livers are immediately removed and frozen for additional analysis. To get blood, punctures are made in the hearts of the unconscious animals[1]. |
| References |
[1]. Inhibition of human hepatitis B virus (HBV) by a novel non-nucleosidic compound in a transgenic mouse model. Antiviral Res. 2002 May;54(2):69-78. [2]. BAY 41-4109 has multiple effects on Hepatitis B virus capsid assembly. J Mol Recognit. 2006 Nov-Dec;19(6):542-8. [3]. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication by Bay 41-4109 and its association with nucleocapsid disassembly. J Chemother. 2008 Aug;20(4):458-67. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : ≥ 37 mg/mL (~93.49 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5268 mL | 12.6339 mL | 25.2678 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5054 mL | 2.5268 mL | 5.0536 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2527 mL | 1.2634 mL | 2.5268 mL |