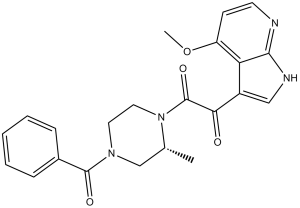
BMS-378806 (also known as BMS 806) is a novel, potent, orally bioavailable small molecule that selectively inhibits the binding of HIV-1 gp120 to the CD4 receptor with EC50 of 0.85-26.5 nM in HIV virus. BMS-378806 inhibits the first step of HIV-1 infection by blocking the binding of host cell CD4 with viral gp120 protein. It binds the exterior envelope glycoprotein gp120, which can block the conformational change that occurs with CD4 binding and preventing fusion of the viral and target cell membranes.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C22H22N4O4 | |
| Molecular Weight | 406.43 | |
| Exact Mass | 406.164 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 65.01; H, 5.46; N, 13.78; O, 15.75 | |
| CAS # | 357263-13-9 | |
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID | 5495818 | |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | |
| Boiling Point | 622.3ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Flash Point | 330.2ºC | |
| Index of Refraction | 1.647 | |
| LogP | 0.73 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 | |
| Complexity | 666 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 | |
| SMILES | COC1=C2C(NC=C2C(C(N3CCN(C[C@H]3C)C(C4=CC=CC=C4)=O)=O)=O)=NC=C1 |
|
| InChi Key | FCBQJNCAKZSIAH-NDEPHWFRSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C21H23FN2O3S/c22-17-3-1-15(2-4-17)13-16-7-9-24(10-8-16)11-12-28(26)18-5-6-19-20(14-18)27-21(25)23-19/h1-6,14,16H,7-13H2,(H,23,25)/t28-/m0/s1 | |
| Chemical Name | 4-benzoyl-1-((4-methoxy-1H- pyrrolo(2,3-b)pyridin-3-yl)oxoacetyl)-2- (R)-methylpiperazine | |
| Synonyms | BMS-378806; BMS 378806; BMS378806; BMS-806; BMS806; Bms 806. | |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | HIV-1;HIV-2 | ||
| ln Vitro | BMS-806, a 7-azaindole derivative, binds gp120 and interferes with the interaction of HIV surface protein gp120 with the host cell receptor CD4. BMS-806 inhibits a panel of macrophage- and T cell-tropic HIV-1 strains, which are laboratory strains that use either CCR5 (M-tropic) or CXR4 (T-tropic) co-receptors to enter cells and are classified as B subtypes. The aqueous solubility from the crystalline form of BMS-806 (BMS 378806) is 170 μg/mL. The solubility of BMS-806 is 1.3 mg/mL at pH=2.1 and 3.3 mg/mL at pH=11, a solubility profile that reveals the amphoteric nature of BMS-806 and estimates the pKa of the protonated form as 2.9 while that of the free base is approximately 9.6. BMS-806 competes with soluble CD4 binding to a monomeric form of gp120 in an ELISA assay with IC50 = ~ 100 nM. BMS-806 is specific towards HIV-1, with no significant inhibitory activity against HIV-2, SIV, MuLV, RSV, HCMV, BVDV, VSV, and influenza virus observed at concentrations ranging from 10 to 30 μM and no overt cytotoxicity toward host cells, CC50 values > 225 μM. BMS-806 binds directly to gp120 at a stoichiometry of approximately 1:1, with a binding affinity similar to that of soluble CD4. The potential BMS-806 target site is localized to a specific region within the CD4 binding pocket of gp120 by using HIV-1 gp120 variants carrying either compound-selected resistant substitutions or gp120-CD4 contact site mutations. | ||
| ln Vivo |
|
||
| Enzyme Assay | In general, host cells are infected with HIV-1 at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 0.005 50% tissue culture infective doses (TCID50)/cell followed by incubation in the presence of serially diluted inhibitors for 4 to 7 days. Virus yields are quantitated using an RT assay or a p24 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (NEN). The results from at least three experiments are used to calculate the 50% effective concentrations (EC50s). The EC50s of IDV, SQV, RTV, and NFV are compared to that of BMS-806 using Dunnetts test. These comparisons are made separately within each assay system. Dunnetts test is used to reduce the probability of false-positive results when a number of treatments are being compared to a control. Confidence bounds for the fold increases in EC50s observes when the same drug is tested in two different assay systems are computed using Fiellers theorem. The use of this theorem is necessary because ratios of parameters (in this case, EC50s) are known not to follow a standard probability distribution, such as the normal distribution. Numbers within the confidence interval are not significantly different from the observed fold increase at the 95% level. | ||
| Cell Assay | To determine cytotoxicity, MT-2 cells are incubated in the presence of serially diluted BMS-806 for 6 days and cell viability is quantitated using an XTT [2,3-bis(2-methoxy-4-nitro-5-sulfophenyl-2H-tetrazolium-5-carboxanilide] assay to calculate the 50% cytotoxic concentrations (CC50s). | ||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| References |
[1]. Discovery of 4-benzoyl-1-[(4-methoxy-1H- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)oxoacetyl]-2- (R)-methylpiperazine (BMS-378806): a novel HIV-1 attachment inhibitor that interferes with CD4-gp120 interactions. J Med Chem. 2003 Sep 25;46(20):4236-9. [2]. Envelope conformational changes induced by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 attachment inhibitors prevent CD4 binding and downstream entry events. J Virol. 2006 Apr;80(8):4017-25. [3]. Biochemical and genetic characterizations of a novel human immunodeficiency virus type 1 inhibitor that blocks gp120-CD4 interactions. J Virol. 2003 Oct;77(19):10528-36 |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO : 50~81 mg/mL ( 123.02~199.29 mM ) Ethanol : ~81 mg/mL |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.15 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.15 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 1.67 mg/mL (4.11 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 16.7 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: 30% PEG400+0.5% Tween 80+5% propylene glycol: 30mg/ml (73.81mM) (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4604 mL | 12.3022 mL | 24.6045 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4921 mL | 2.4604 mL | 4.9209 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2460 mL | 1.2302 mL | 2.4604 mL |