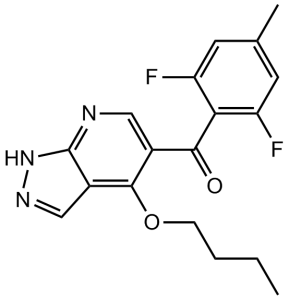
BMS-265246 (BMS265246; BMS 265246) is a novel, potent and selective CDK1/2 (Cyclin-dependent kinases) inhibitor with potential antitumor activity. In a cell-free assay, it inhibits CDK1/2 with IC50s of 6 nM/9 nM. It inhibits CDK1/2 25 times more selectively than CDK4 does.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C18H17F2N3O2 | |
| Molecular Weight | 345.34 | |
| Exact Mass | 345.128 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 62.60; H, 4.96; F, 11.00; N, 12.17; O, 9.27 | |
| CAS # | 582315-72-8 | |
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID | 135402864 | |
| Appearance | White to pink solid powder | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | |
| Boiling Point | 552.9±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Flash Point | 288.2±30.1 °C | |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C | |
| Index of Refraction | 1.595 | |
| LogP | 3.51 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 25 | |
| Complexity | 456 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 | |
| SMILES | FC1C([H])=C(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])=C(C=1C(C1C([H])=NC2C(=C([H])N([H])N=2)C=1OC([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])=O)F |
|
| InChi Key | SCFMWQIQBVZOQR-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C18H17F2N3O2/c1-3-4-5-25-17-11(8-21-18-12(17)9-22-23-18)16(24)15-13(19)6-10(2)7-14(15)20/h6-9H,3-5H2,1-2H3,(H,21,22,23) | |
| Chemical Name | (4-butoxy-2H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridin-5-yl)-(2,6-difluoro-4-methylphenyl)methanone | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | CDK1/cycB (IC50 = 6 nM); CDK2/Cyc E (IC50 = 9 nM); CDK4/cycD (IC50 = 230 nM) | ||
| ln Vitro | BMS265246 blocks A2780 Cytox with an IC50 of 0.76 μM and suppresses CDK4/cycD activity with an IC50 of 0.23 μM. The inhibitor, BMS265246, binds to CDK2 and exhibits coincidental occupancy with the ATP purine binding site. It also forms significant H-bonds with Leu83 on the protein backbone. The CDK1 and CDK2 potencies of BMS265246 are 25 and 11 times more potent than those of CDK1 and CDK2, respectively. The most effective CDK/CDK2 selective analogue from this chemotype is BMS265246.[1] According to a recent study, BMS-265246 inhibits HCT-116 cell proliferation, with an EC50 ranging from 0.293 μM to 0.492 μM. Following BMS-265246 treatment, G2-arrested cells with large round nuclei, low DNA intensity, and 4N DNA content constituted the predominant cell populations.[2] | ||
| ln Vivo |
|
||
| Enzyme Assay | The reaction mixture for the kinase reaction is 50 μL of kinase buffer (50 mM Tris, pH 8.0, 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EGTA, 0.5 mM DTT), 100 ng of baculovirus-expressed GST-CDK1/cyclin B1 complex, 1 μg histone H1, 0.2 μCi 33P γ-ATP, and 25 }M ATP. The addition of cold trichloroacetic acid (TCA) to a final concentration of 15% ends the 45-minute incubation period at 30 Celsius. Utilizing a Filtermate universal harvester, TCA precipitates are gathered onto GF/C unifilter plates. A TopCount 96 well liquid scintillation counter is used to quantify the filters. The concentration needed to block 50% of kinase activity (IC50) is found using dose response curves. Six concentrations of BMS265246 are tested in triplicate after being dissolved at a concentration of 10 mM in DMSO. 2% is the final DMSO concentration in the experiment. IC50 values have a coefficient of variance (SD/mean, n = 6) = 16% and are obtained using nonlinear regression analysis. | ||
| Cell Assay | Plates with 96 wells are used to hold HCT-116 cells. Cell density for each well is determined by averaging the number of objects (cells) for each field of view for that particular well. Cell density for a treatment compound is converted to a percentage in relation to the DMSO treatment's plate-averaged cell density (i.e., 100% represents the average cell density for DMSO treatment). Utilizing TIBCO Spotfire, logistic regression curve fits are performed; the concentration at which the curve crosses 50% is the BMS-265246 EC50. | ||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| References |
[1]. Bioorg Med Chem Lett . 2003 Jul 21;13(14):2405-8. [2]. Mol Cancer Ther . 2011 Feb;10(2):242-54. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: 2.08 mg/mL (6.02 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with sonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 1.25 mg/mL (3.62 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 12.5 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 3: 30% PEG400+0.5% Tween80+5% Propylene glycol : 30mg/mL (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8957 mL | 14.4785 mL | 28.9570 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5791 mL | 2.8957 mL | 5.7914 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2896 mL | 1.4478 mL | 2.8957 mL |