Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C70H106N8O14S |
| Molecular Weight | 1315.70 |
| Appearance | Typically exists as solid at room temperature |
| Synonyms | V10; V-10 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | MDM2 |
| ln Vitro |
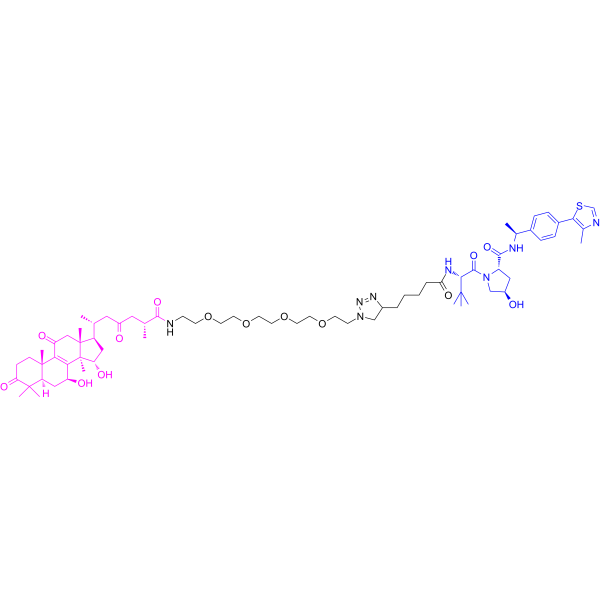
In this study, two series of novel GAA PROTACs C1–C10 and V1–V10 were designed and synthesized for the treatment of breast cancer. The antitumor activity of these compounds was evaluated against four human tumor cell lines (MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, SJSA-1, and HepG2). Among them, V9 and V10 showed stronger anti-proliferative effects against breast cancer cells, and Antitumor agent-150 (V10) showed the best selectivity in MDA-MB-231 cells (TNBC), which was 5-fold higher than that of the lead compound GAA. Preliminary structure-activity analysis revealed that V-series GAA PROTACs had better effects than C-series, and the introduction of 2O–4O PEG linkers could significantly improve the antitumor activity. Molecular docking, surface plasmon resonance (SPR), cellular thermal shift assay (CETSA), and Western blot researches showed that both V9 and V10 could bind with MDM2, and degrade the protein through the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Molecular dynamics simulation (MD) revealed that V10 is a bifunctional molecule that can bind to von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) at one end and target MDM2 at the other. In addition, V10 promoted the upregulation of p21 in p53-mutant MDA-MB-231 cells, and induced apoptosis via down-regulation of the bcl-2/bax ratio and the expression of cyclin B1.[1] Antitumor agent-150 (V10) showed good antitumor activity in the TNBC zebrafish model, with an inhibition rate of 27.2% at 50 μg/mL[1]. Antitumor agent-150 (V10, 10 μM) promoted apoptosis of MDA-MB-231 cells[1]. Antitumor agent-150 (V10) treatment significantly altered the G1 and S phases of MDA-MB-231 cells[1]. |
| ln Vivo | In vivo experiments showed that, Antitumor agent-150 (V10) also exhibited good tumor inhibitory activity in xenografted TNBC zebrafish models, with an inhibition rate of 27.2% at 50 μg/mL. In conclusion, our results suggested that V10 has anti-tumor effects on p53-mutant breast cancer in vitro and in vivo, and may be used as a novel lead compound for the future development of TNBC.[1] |
| Enzyme Assay |
SPR[1] The interaction of compound V9 and V10 with MDM2 protein was detected by molecular interaction analyzer. MDM2 protein (50 μg/mL) was immobilized on a PCH sensor chip and pre-activated for 600 s using an EDC/NHS mixture at a flow rate of 10 μL/min. Dilute V9 or V10 to 0, 3.13, 6.25, 12.5, 25, 50, 100 μM with PBST buffers containing 5% DMSO and 0.005% Tween. The binding time was 400 s, and the flow rate was 15 μL/min. The dissociation time was 60 s, and the affinity constant KD value was obtained by computer fitting and steady-state analysis. |
| Cell Assay |
Cell viability assay[1] The anti-proliferation activity of the compound against MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, SJSA-1, HepG2 and HT-22 cells was determined by MTT Cell Proliferation Assay Kit. A cell suspension with a volume of 100 μL was added into the 96-well plate, with approximately 5 × 103 cells per well. The culture plates were pre-cultured at 37 °C in an incubator with 5% CO2 by volume percentage for 24 h. On the next day, the original medium was discarded, and 100 μL of medium containing different concentrations of GAA derivatives or 5 μM of the positive drug hydroxydaunorubicin hydrochloride (DOX) was added to the 96-well plates, and incubated in the incubator for 48 h or 72 h. After the corresponding time of administration, 10 μL MTT solution was added to each well. After the culture plate was incubated in the incubator for 4 h, the original medium was discarded, and then 150 μL DMSO was added. After the culture plate was shaken at low speed for 10 min, the absorbance at 490 nm of each hole was measured by the microplate reader, and the cell viability in each well was presented as percentage of control cells.[1] |
| Animal Protocol |
Determination of MTC in zebrafish and establishment of xenograft tumor model[1] Wild type AB strain zebrafish embryos were fed in fish culture water at 28 °C (Water quality: 200 mg of instant sea salt per 1 L of reverse osmosis water, conductivity 450–550 μS/cm, pH 6.5–8.5, and hardness 50–100 mg/L CaCO3), the experimental animal use license number was SYXK (Zhe) 2022–0004. This research was approved by the international certification of Association for Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care (AAALAC). Wild type AB strain zebrafish were randomly selected 3 dpf days after fertilization in 6-well plates, and 30 zebrafish were treated in each well. In addition to the normal control group, the other concentration groups were given V10 in water solution, and the normal control group was set up with a capacity of 3 mL per well. After treatment at 35 °C for 2 days, the MTC of V10 in normal zebrafish was determined.[1] MDA-MB-231 cells labeled with CM-DiI were transplanted into the yolk sac of 2 dpf wild type AB strain zebrafish by microinjection, and about 200 cells were transplanted into each tail to establish a zebrafish tumor transplantation model. The model zebrafish was placed at 35 °C and cultured to 3 dpf. At 3 dpf, zebrafish with good consistency of transplanted tumor cells were selected under the microscope and randomly assigned to 6-well plates with 30 cells per well. V10 was given in water solution, the cisplatin concentration in positive control was 15.0 μg/mL, and the model control group was set up with a capacity of 3 mL per well. After treatment at 35 °C for 2 days, 10 zebrafish were randomly selected from each experimental group and photographed under a fluorescence microscope. Data were collected using NIS-Elements D 3.20 advanced image processing software to analyze the fluorescence intensity of tumor cells, and the anti-tumor growth efficacy of V10 was evaluated based on the statistical analysis results of this index. The statistical results were expressed as mean ± SE. |
| References |
[1]. Discovery of ganoderic acid A (GAA) PROTACs as MDM2 protein degraders for the treatment of breast cancer. Eur J Med Chem. 2024 Apr 15:270:116367. |
| Additional Infomation | In conclusion, two series of GAA PROTACs C1–C10 and V1–V10 were designed and synthesized as potent MDM2 protein degraders for the treatment of breast cancer. Screening results showed that V9 and V10 had stronger anti-proliferative effects on breast cancer cells, including an inhibition rate of 83.1% for V10 in TNBC (MDA-MB-231 cells), which was better than the lead compound GAA. Structure-activity relationships indicated that the introduction of 2O–4O PEG linkers could significantly improve the antitumor activity. Further investigation of the degradation properties revealed that both V9 and V10 could bind to MDM2 and degrade the protein through the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Among them, V10 can degrade MDM2 and increase the expression of p21 in TNBC. MD Simulations results proved the ternary complex of MDM2/V10/VHL is stable. In addition, V10 promoted the downregulation of bcl-2/bax and cyclin B1 expression, induced cell arrest in G1-S and G2-M phases, and ultimately led to cell apoptosis. In vivo experiments showed that V10 exhibited lower toxicity and significant anticancer activity with an inhibition rate of 27.2% at a dose concentration of 50 μg/mL. Therefore, the GAA PROTACs can not only avoid the drug resistance caused by MDM2-p53 negative feedback through MDM2 protein degradation, but also overcome the treatment difficulty caused by p53 mutation or inactivation in TNBC ( Fig. 11 ). Based on the above results, our study demonstrated that the GAA MDM2 degrader agent V10 designed using the PROTAC strategy can enhance the anti-tumor activity of GAA, and it can be further developed and investigated as a MDM2 protein degrader for the treatment of TNBC.[1] |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.7601 mL | 3.8003 mL | 7.6005 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.1520 mL | 0.7601 mL | 1.5201 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.0760 mL | 0.3800 mL | 0.7601 mL |