Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C58H80CL2N8O8 |
| Exact Mass | 1086.547 |
| CAS # | 1883545-51-4 |
| Related CAS # | AZD5582;1258392-53-8 |
| PubChem CID | 90489014 |
| Appearance | Off-white to light yellow solid |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 10 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 19 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 76 |
| Complexity | 1950 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 10 |
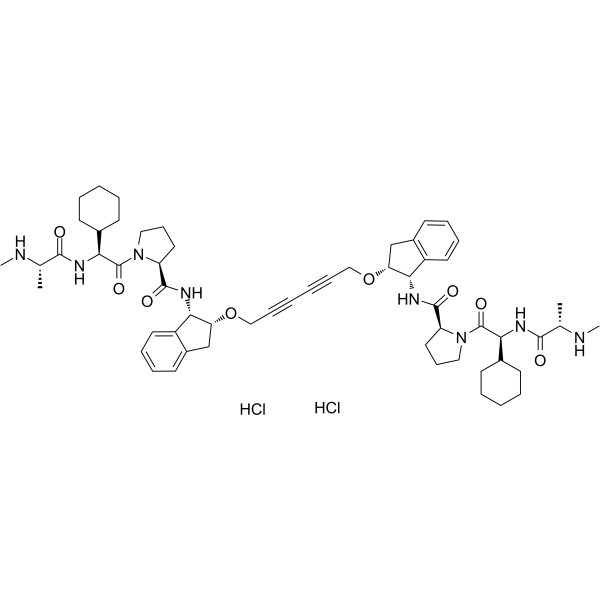
| SMILES | C[C@@H](C(=O)N[C@@H](C1CCCCC1)C(=O)N2CCC[C@H]2C(=O)N[C@@H]3[C@@H](CC4=CC=CC=C34)OCC#CC#CCO[C@@H]5CC6=CC=CC=C6[C@@H]5NC(=O)[C@@H]7CCCN7C(=O)[C@H](C8CCCCC8)NC(=O)[C@H](C)NC)NC.Cl.Cl |
| InChi Key | DAILKFFMJFAUCE-GXSVUDMFSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C58H78N8O8.2ClH/c1-37(59-3)53(67)61-49(39-21-9-7-10-22-39)57(71)65-31-19-29-45(65)55(69)63-51-43-27-15-13-25-41(43)35-47(51)73-33-17-5-6-18-34-74-48-36-42-26-14-16-28-44(42)52(48)64-56(70)46-30-20-32-66(46)58(72)50(40-23-11-8-12-24-40)62-54(68)38(2)60-4;;/h13-16,25-28,37-40,45-52,59-60H,7-12,19-24,29-36H2,1-4H3,(H,61,67)(H,62,68)(H,63,69)(H,64,70);2*1H/t37-,38-,45-,46-,47+,48+,49-,50-,51-,52-;;/m0../s1 |
| Chemical Name | (2S)-1-[(2S)-2-cyclohexyl-2-[[(2S)-2-(methylamino)propanoyl]amino]acetyl]-N-[(1S,2R)-2-[6-[[(1S,2R)-1-[[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-cyclohexyl-2-[[(2S)-2-(methylamino)propanoyl]amino]acetyl]pyrrolidine-2-carbonyl]amino]-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-2-yl]oxy]hexa-2,4-diynoxy]-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-yl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide;dihydrochloride |
| Synonyms | AZD5582 dihydrochloride |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: This product requires protection from light (avoid light exposure) during transportation and storage. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | cIAP1 (IC50 = 15 nM); cIAP2 (IC50 = 21 nM); XIAP (IC50 = 15 nM) |
| ln Vitro |
In H1975 NSCLC cells, AZD5582 (20 nM; 48 hours) inhibits cell viability by working with IFNγ or viral double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)[2]. Caspase-3 and caspase-7 are cleaved by AZD5582 (20 nM; 17 or 25 hours), which also activates RIPK1 (a downstream regulator of caspase-8) and the extrinsic (caspase-8) and intrinsic (caspase-9) apoptosis pathways[2]. AZD5582 (20 nM; 48 hours) causes apoptosis. Due to the co-treatment of HCC827 NSCLC cells with AZD5582 and IFN, which results in the induction of cell death and active caspase-3/8 activities.[2] |
| ln Vivo | AZD5582 (intravenous injection; 0.1-3.0 mg/kg; once a week; 2 weeks) causes degradation of cIAP1 and caspase 3 cleavage in tumor cells, and after a two-week course of treatment, the tumors largely disappeared. When mice are given a medium dose of AZD5582 (0.5 mg/kg), cIAP1 degrades immediately after administration, but it takes some time to have an effect that induces apoptosis[1]. |
| Animal Protocol |
MDA-MB-231 xenograft-bearing mice[1] 0.1 mg/kg, 0.5 mg/kg, 3.0 mg/kg Intravenous injection; once a week; 2 weeks |
| References |
[1]. Discovery of a novel class of dimeric Smac mimetics as potent IAP antagonists resulting in a clinical candidate for the treatment of cancer (AZD5582). J Med Chem. 2013 Dec 27;56(24):9897-919. [2]. IF-γ and Smac mimetics synergize to induce apoptosis of lung cancer cells in a TNFα-independent manner,Cancer Cell Int. 2018; 18: 84. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: ≥50 mg/mL (~46 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (2.30 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (2.30 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (2.30 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |