AZ31 (AZ-31; AZ 31) is a novel, potent and orally bioavailable and BBB (blood-brain barrier)-penetreable ATM inhibitor with antitumor activity. In cell-free assays, it inhibits ATM with an IC50 in the nanomolar range. Assays for drug screening and lead compound refinement led to its identification. Inhibiting ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM) during glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) radiation therapy may enhance tumor control by preventing the body's reaction to DNA damage brought on by radiation. The limited bioavailability of current inhibitors in the central nervous system (CNS) is a significant barrier to their clinical implementation; therefore, finding ATM inhibitors (ATMi) with enhanced CNS penetration was the aim. The effectiveness of AZ31 and its effects on tumors and healthy brain were examined in vivo. AZ31 enhanced blood-brain barrier (BBB) penetration, radiosensitized GBM cells in vitro, and inhibited the DNA damage response. Moreover, human glioma cell lines with checkpoint-defective mutations or mutant p53 expressed were more susceptible to ATMi radiosensitization. The p53 effect is explained by a tendency for cells to experience a mitotic catastrophe in comparison to cells that have p53 that is wild-type.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C24H28N4O3 | |
| Molecular Weight | 420.504125595093 | |
| Exact Mass | 420.22 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 68.55; H, 6.71; N, 13.32; O, 11.41 | |
| CAS # | 2088113-98-6 | |
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID | 134694318 | |
| Appearance | Off-white to light yellow solid powder | |
| LogP | 2.9 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 31 | |
| Complexity | 585 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 | |
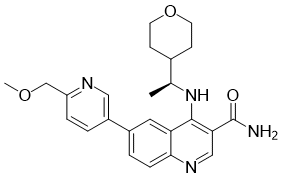
| SMILES | C[C@@H](C1CCOCC1)NC2=C3C=C(C=CC3=NC=C2C(=O)N)C4=CN=C(C=C4)COC |
|
| InChi Key | DISRGUXSEDBDDN-HNNXBMFYSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C24H28N4O3/c1-15(16-7-9-31-10-8-16)28-23-20-11-17(18-3-5-19(14-30-2)26-12-18)4-6-22(20)27-13-21(23)24(25)29/h3-6,11-13,15-16H,7-10,14H2,1-2H3,(H2,25,29)(H,27,28)/t15-/m0/s1 | |
| Chemical Name | 6-[6-(methoxymethyl)pyridin-3-yl]-4-[[(1S)-1-(oxan-4-yl)ethyl]amino]quinoline-3-carboxamide | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: This product requires protection from light (avoid light exposure) during transportation and storage. |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | ATM ( IC50 = 1.2 nM ); ATM ( IC50 = 46 nM ) | |
| ln Vitro |
|
|
| ln Vivo |
|
|
| Enzyme Assay | Compounds were dispensed by acoustic dispensing into assay plates in 100% DMSO. The ATM enzyme was added to a Hepes buffer (50 mM HEPES pH 7.4, 150 mM NaCl, 10 mM, MnCl2 1 mM, DTT, 5% v/v Glycerol, 0.05% v/v Tween 20) and left for 30 minutes to preincubate before the substrate solution containing p53 and ATP was added. Following two hours, the enzyme reaction was halted by adding the detection reagent (33 mM HEPES pH 7.4, 20 mM EDTA, 0.1 M KF, 0.1 mg/mL BSA, 13 nM D2 Anti-GST antibody (Cisbio), and 0.5 nM Eu3+ Anti-p53phosphoS15 antibody). The mixture was then incubated for an additional night before being read using a standard HTRF filter block method on a Pherastar instrument. In the assay, the final concentrations of p53, ATP, and DMSO were 50 nM, 5 µM, and 1%, respectively. The data analysis software's four parameter fit method, or smart fitting model, was used to calculate the IC50 values, or the concentrations of the test compound that inhibited 50% of the enzyme's activity. | |
| Cell Assay | Proliferation was assessed using an SRB assay after six CRC cell lines were treated with AZ31 (dose 1.25, 2.5, or 5 μmol/L), SN38 (0.3125 – 20 nM), or AZ31 + SN38. | |
| Animal Protocol |
CRC PDX models (Four-to-six week-old female athymic nude mice with implanted patient-derived colorectal adenocarcinoma tumor) 100 mg/kg-daily × 3 by oral gavage |
|
| References |
[1]. Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 19; 8(67): 110904–110913. [2]. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 13, 6281–6292 |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3781 mL | 11.8906 mL | 23.7812 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4756 mL | 2.3781 mL | 4.7562 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2378 mL | 1.1891 mL | 2.3781 mL |