Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C19H16FNO4 |
| Exact Mass | 341.106 |
| CAS # | 2136579-33-2 |
| PubChem CID | 137642579 |
| Appearance | White to yellow solid powder |
| LogP | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 25 |
| Complexity | 528 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| InChi Key | YNGXWVIJSUJZSG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C19H16FNO4/c20-14-6-3-12(4-7-14)2-1-9-21-18(23)16-10-13-5-8-15(22)11-17(13)25-19(16)24/h3-8,10-11,22H,1-2,9H2,(H,21,23) |
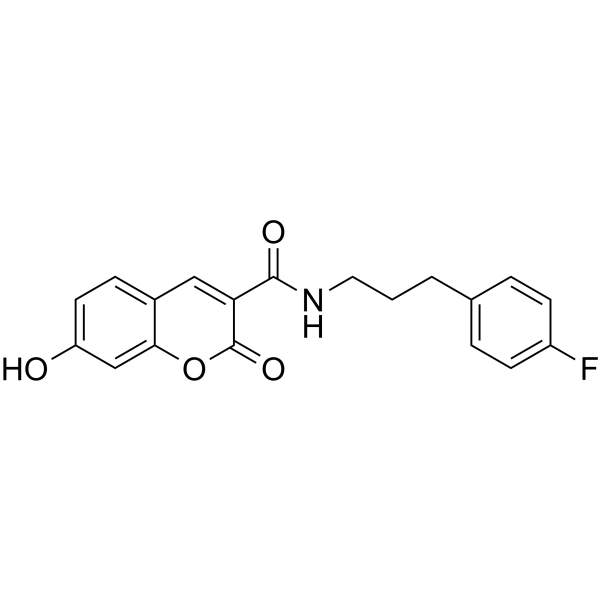
| Chemical Name | N-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)propyl]-7-hydroxy-2-oxochromene-3-carboxamide |
| Synonyms | AKR1B10-IN-1; 2136579-33-2; CHEMBL4089817; N-(3-(4-Fluorophenyl)propyl)-7-hydroxycoumarin-3-carboxamide; |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | AKR1B10 (Aldo-Keto Reductase 1B10); AKR1B10 (IC50 = 3.5 nM); AKR1B1 (IC50 = 277 nM)[1] |
| ln Vitro | AKR1B10-IN-1 (compound 4e) reduces A549 and A549/1B10 cell growth in a dose-dependent manner[1]. By overexpressing both AKR1B10 and the endogenous protein, AKR1B10-IN-1 (compound 4e) (0-20 μM; 96 hours) totally suppresses enhanced cell proliferation[1]. Compound 4e, AKR1B10-IN-1 (0-40 μM; 26 hours; pretreatment with AKR1B10-IN-1 for 2 hours, followed by 24 hours of CDDP incubation) reduces CDDP-R-A549 cell viability in a dose-dependent way[1]. |
| Cell Assay |
Cell Viability Assay[1] Cell Types: A549 cells, A549/1B10 cells (AKR1B10- stably overexpressing A549 cells) Tested Concentrations: 0, 10, 20 μM Incubation Duration: 96 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Dose-dependently suppressed the growth of both A549 and A549/1B10 cells, and statistically significant at 20 μM. Cell Viability Assay[1] Cell Types: CDDP-resistance (cisplatin-resisitance) of A549 cells Tested Concentrations: 0, 10, 20, 40 μM Incubation Duration:Pretreatment with AKR1B10-IN-1 for 2 hrs (hours), then incubated with CDDP for 24 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: diminished the cell viability of CDDP-R-A549 cells in a dose-dependent manner, and most obvious in the treatment of 40 μM. |
| References |
[1]. Synthesis of Potent and Selective Inhibitors of Aldo-Keto Reductase 1B10 and Their Efficacy against Proliferation, Metastasis, and Cisplatin Resistance of Lung Cancer Cells. J Med Chem. 2017 Oct 26;60(20):8441-8455. |
| Additional Infomation | Aldo-keto reductase 1B10 (AKR1B10) is overexpressed in several extraintestinal cancers, particularly in non-small-cell lung cancer, where AKR1B10 is a potential diagnostic marker and therapeutic target. Selective AKR1B10 inhibitors are required because compounds should not inhibit the highly related aldose reductase that is involved in monosaccharide and prostaglandin metabolism. Currently, 7-hydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenylimino)-2H-chromene-3-carboxylic acid benzylamide (HMPC) is known to be the most potent competitive inhibitor of AKR1B10, but it is nonselective. In this study, derivatives of HMPC were synthesized by removing the 4-methoxyphenylimino moiety and replacing the benzylamide with phenylpropylamide. Among them, 4c and 4e showed higher AKR1B10 inhibitory potency (IC50 4.2 and 3.5 nM, respectively) and selectivity than HMPC. The treatments with the two compounds significantly suppressed not only migration, proliferation, and metastasis of lung cancer A549 cells but also metastatic and invasive potentials of cisplatin-resistant A549 cells.[1] |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |