Physicochemical Properties
| Exact Mass | 326.12665 |
| CAS # | 1035154-46-1 |
| PubChem CID | 168448551 |
| Appearance | Typically exists as solid at room temperature |
| LogP | 1.9 |
| InChi Key | APJYZRJDCRLKDI-RIYZIHGNSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C18H18N2O4/c1-9-12(4-6-17(22)23)10(2)19-16(9)8-14-13-7-11(21)3-5-15(13)20-18(14)24/h3,5,7-8,19,21H,4,6H2,1-2H3,(H,20,24)(H,22,23)/b14-8+ |
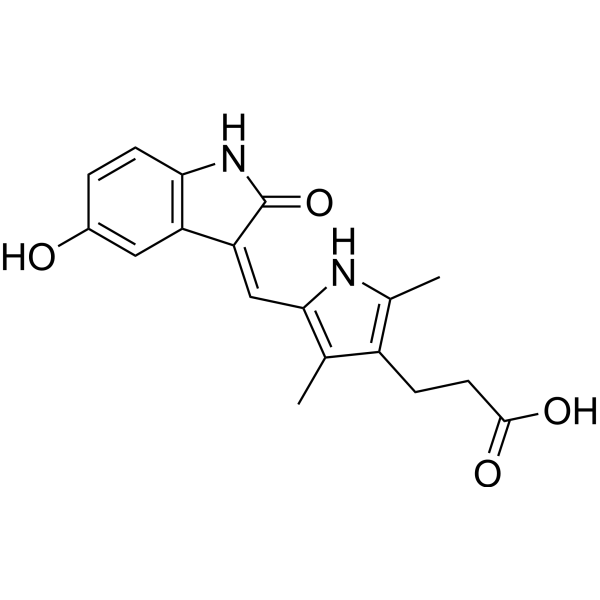
| Chemical Name | 3-[5-[(E)-(5-hydroxy-2-oxo-1H-indol-3-ylidene)methyl]-2,4-dimethyl-1H-pyrrol-3-yl]propanoic acid |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | RTK/receptor tyrosine kinases |
| ln Vitro | (Z)-5-[(1,2-Dihydro-2-oxo-3H-indol-3-ylidene)methyl]-2,4-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-3-propanoic acid (TSU-68) is a new anticancer drug that inhibits angiogenic receptor tyrosine kinases, which play a crucial role in tumor-induced vascularization. TSU-68 undergoes hepatic oxidation and glucuronidation. Incubation of TSU-68 with human liver microsomes in the presence of NADPH resulted in the formation of three major metabolites: 5-, 6-, and 7-hydroxyindolinone derivatives. The 5-, 6-, and 7-hydroxylation followed simple Michaelis-Menten kinetics with V(max)/K(m) values (an indicator of intrinsic clearance) of 13, 25, and 6 microl/min/mg, respectively. Of the 10 cDNA-expressed human cytochrome P450 isoforms examined, only CYP1A1 and CYP1A2 exhibited appreciable TSU-68 hydroxylation activity. Inhibition studies with alpha-naphthoflavone (a selective CYP1A2 inhibitor) and anti-CYP1A2 antibody also indicated the almost exclusive role of CYP1A2 in microsomal TSU-68 hydroxylation. Treatment of human hepatocytes with 10 microM TSU-68 resulted in a 28- to 140-fold increase in CYP1A1/2-mediated ethoxyresorufin O-deethylase activity. The protein levels of CYP1A2 were increased in TSU-68-treated hepatocytes, and those of CYP1A1, which were undetectable in control hepatocytes, were also increased to detectable levels in the TSU-68-treated hepatocytes. Thus, TSU-68 was shown to induce CYP1A1/2 expression, which was responsible for its hydroxylation. The observation that TSU-68 treatment resulted in a 10- to 45-fold increase in 5-, 6-, and 7-hydroxylation directly demonstrated the autoinduced hydroxylation of TSU-68. In conclusion, TSU-68 has the potential to cause induction of its own CYP1A1/2-mediated oxidative metabolism in humans. This autoinductive effect provides a clear explanation for the clinically observed decrease in TSU-68 plasma concentrations during repeated administration of the drug.[1] |
| References |
[1]. Identification of Human Liver Cytochrome P450 Isoforms Involved in Autoinduced Metabolism of the Antiangiogenic Agent (Z)-5-[(1,2-Dihydro-2-oxo-3H-indol-3-ylidene)methyl]-2,4-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-3-propanoic Acid (TSU-68). Drug Metabolism and Disposition June 2008, 36 (6) 1003-1009. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |