Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C25H24O12 |
| Molecular Weight | 516.4509 |
| Exact Mass | 516.126 |
| CAS # | 57378-72-0 |
| PubChem CID | 6474309 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 810.8±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 140 °C |
| Flash Point | 274.9±27.8 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.719 |
| LogP | 0.89 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 12 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 37 |
| Complexity | 887 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
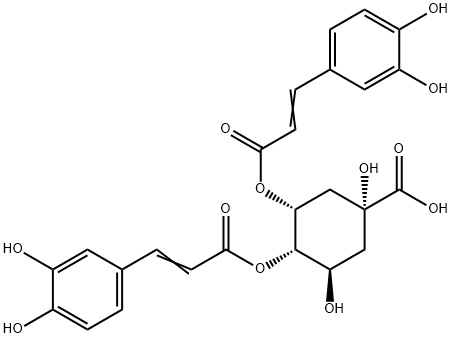
| SMILES | C1[C@H]([C@@H]([C@@H](C[C@]1(C(=O)O)O)OC(=O)/C=C/C2=CC(=C(C=C2)O)O)OC(=O)/C=C/C3=CC(=C(C=C3)O)O)O |
| InChi Key | UFCLZKMFXSILNL-RVXRWRFUSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C25H24O12/c26-15-5-1-13(9-17(15)28)3-7-21(31)36-20-12-25(35,24(33)34)11-19(30)23(20)37-22(32)8-4-14-2-6-16(27)18(29)10-14/h1-10,19-20,23,26-30,35H,11-12H2,(H,33,34)/b7-3+,8-4+/t19-,20-,23+,25-/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (1R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-bis[[(E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoyl]oxy]-1,5-dihydroxycyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid |
| Synonyms | Isochlorogenic acid C |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| ln Vitro |
DU-145 prostate cancer cells are susceptible to dose-dependent inhibitory activity from 4,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid (0.1~100 µM; 72 h), which also induces cell cycle arrest and Bcl-2 inactivation[2]. When administered at concentrations of 10 to 100 µg/mL, 4,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid (1~100 µg/mL; 48 h) significantly increases cell viability in D-GalN-challenged HL-7702 hepatocytes by preventing apoptosis.The maximum inhibition rates of 4,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid (1~100 µg/mL; 4 days) on the expressions of HBsAg and HBeAg are 86.93 and 59.79%, respectively. This is a significant inhibition of HBsAg and HBeAg expressions[3]. |
| ln Vivo | In type 2 diabetic mice, 4,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid effectively reduces glycemia and insulin resistance and improves insulin sensitivity by increasing the expression of GLUT2, GK, and PDX-1 protein[1]. |
| Cell Assay |
Cell Line: HL-7702 hepatocytes (exposure to 80 mM D-GalN for 6h) Concentration: 1~100 μg/mL Incubation Time: 48 h Result: produced a maximum protection rate of 47.28% at 100 µg/mL and greatly increased cell viability at concentrations of 10 to 100 µg/mL. |
| References |
[1]. Gynura divaricata rich in 3, 5-/4, 5-dicaffeoylquinic acid and chlorogenic acid reduces islet cell apoptosis and improves pancreatic function in type 2 diabetic mice. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2018 Oct 10;15:73. [2]. Inhibition of Prostate Cancer Cells by 4,5-Dicaffeoylquinic Acid through Cell Cycle Arrest. Prostate Cancer. 2019 May 23;2019:4520645. [3]. Evaluation of anti-apoptotic, anti-injury and antihepatitis B virus effects of isochlorogenic acid C in vitro. Journal of Medicinal Plants Research Vol. 6(16), pp. 3199-3206 30 April, 2012 |
| Additional Infomation |
4,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid is a quinic acid. 4,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid has been reported in Gardenia jasminoides, Farfugium japonicum, and other organisms with data available. See also: Lonicera japonica flower (part of); Stevia rebaudiuna Leaf (part of); 4,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid (annotation moved to). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : ~50 mg/mL (~96.81 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.84 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.84 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.84 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9363 mL | 9.6815 mL | 19.3630 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3873 mL | 1.9363 mL | 3.8726 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1936 mL | 0.9681 mL | 1.9363 mL |