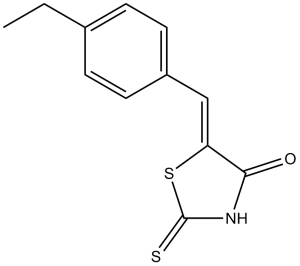
10058-F4 (10058F4; 10058 F4) is a novel potent and selective c-Myc inhibitor with potential antineoplastic activity. It specifically inhibits the protein-protein interaction of c-Myc-Max. In human acute myeloid leukemia, 10058-F4 causes cell-cycle arrest, apoptosis, and myeloid differentiation.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C12H11NOS2 | |
| Molecular Weight | 249.35 | |
| Exact Mass | 249.028 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 57.80; H, 4.45; N, 5.62; O, 6.42; S, 25.72 | |
| CAS # | 403811-55-2 | |
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID | 1271002 | |
| Appearance | Yellow solid powder | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | |
| Boiling Point | 387.1±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Flash Point | 187.9±30.7 °C | |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C | |
| Index of Refraction | 1.664 | |
| LogP | 4.38 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 16 | |
| Complexity | 330 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 | |
| SMILES | O=C1NC(S/C1=C/C2=CC=C(CC)C=C2)=S |
|
| InChi Key | SVXDHPADAXBMFB-JXMROGBWSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C12H11NOS2/c1-2-8-3-5-9(6-4-8)7-10-11(14)13-12(15)16-10/h3-7H,2H2,1H3,(H,13,14,15)/b10-7+ | |
| Chemical Name | (5E)-5-[(4-ethylphenyl)methylidene]-2-sulfanylidene-1,3-thiazolidin-4-one | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | c-Myc |
| ln Vitro | 10058-F4 prevents the growth of leukemic cells and the dimerization of Max and Myc. AML cells undergo apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest upon exposure to 10058-F4. AML cells are stopped at the G0/G1 phase by 10058-F4, which also upregulates the expression of CDK inhibitors p21 and p27 and downregulates c-Myc expression. In the meanwhile, 10058-F4 causes apoptosis by activating the mitochondrial pathway, which is demonstrated by the cleavage of caspase 3, 7, and 9, the release of cytoplasmic cytochrome C, the downregulation of Bcl-2, and the upregulation of Bax. Additionally, 10058-F4 induces myeloid differentiation, possibly by activating several transcription factors. Likewise, primary AML cells exhibited 10058-F4-induced apoptosis and differentiation.[1] 10058-F4 reduces intracellular levels of [alpha]-fetoprotein (AFP), inhibits the growth of HepG2 cells by lowering c-Myc protein levels, and most likely does so by upregulating p21WAF1, an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase (cdk). Additionally, human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) is transcriptionally downregulated upon treatment with 10058-F4. Apart from impeding the growth of HepG2 cells, 10058-F4 also increases susceptibility to doxorubicin, 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), and cisplatin, which are common chemotherapeutic agents.[2] |
| ln Vivo | After a single intravenous dose, peak plasma 10058-F4 concentrations of about 300 μM are observed at 5 min and decreased to below the detection limit at 360 min. The best approximation for plasma concentration versus time data is an open, two-compartment linear model. The tissues with the highest concentrations of 10058-F4 are the kidney, liver, fat, and lung. 10058-F4 tumor peak concentrations are at least ten times lower than plasma peak concentrations. There are eight 10058-F4 metabolites found in the kidney, liver, and plasma. 10058-F4 has a terminal half-life of about one hour and a distribution volume of greater than 200 milliliters per kilogram. Following intravenous administration of 20 or 30 mg/kg 10058-F4, no discernible reduction in tumor growth is observed in the mice.[3] |
| Enzyme Assay | The protooncogene c-Myc plays an important role in the control of cell proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation, and its aberrant expression is frequently seen in multiple human cancers, including acute myeloid leukemia (AML). As c-Myc heterodimerizes with Max to transactivate downstream target genes in leukemogenesis. Inhibition of the c-Myc/Max heterodimerization by the recently identified small-molecule compound, 10058-F4, might be a novel antileukemic strategy[1]. |
| Cell Assay | 10058-F4 concentrations are applied in triplicate to cells plated in 96-well plates (105/mL for cell lines and 5 × 105/mL for primary leukemic cells). Each well receives 20 μL of 5 mg/mL MTT added at different times. Following three hours of incubation at 37°C, 100 μL of DMSO lysis buffer is added and the MTT medium is removed. Using a spectrophotometer with a wavelength of 570 nm, the percentage of treated cell absorbance compared to solvent control cells is used to determine the number of viable cells. |
| Animal Protocol | The following groups are stratified based on the C B-17 SCID mice that are bearing PC-3 human prostate tumor xenografts: vehicle control, positive control (10 mg/kg docetaxel), and 10058-F4 treatment (20 or 30 mg/kg/dose). As per our earlier research, the highest dosage of 10058-F4 that can be tolerated on this regimen is 30 mg/kg. For two weeks, mice receive intravenous treatment five days a week.Tumor volumes and body weights are measured twice a week. The second study uses C B-17 SCID mice that have been stratified into similar treatment groups based on the DU145 human androgen-independent prostate cancer xenografts. Docetaxel is given intravenously every seven days in two doses of 10 mg/kg. It is the positive control used in both efficacy studies. Calipers are used to measure tumors, and TV= L×W2/2 is the formula used to calculate tumor volumes, where L is the largest diameter of the tumor and W is the smallest diameter perpendicular to L. Mice are monitored for tumor regrowth for a minimum of one week after the last dose is administered. |
| References |
[1]. A small-molecule c-Myc inhibitor, 10058-F4, induces cell-cycle arrest, apoptosis, and myeloid differentiation of human acute myeloid leukemia. Exp Hematol. 2006 Nov;34(11):1480-9. [2]. Small-molecule c-Myc inhibitor, 10058-F4, inhibits proliferation, downregulates human telomerase reverse transcriptase and enhances chemosensitivity in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Anticancer Drugs. 2007 Feb;18(2):161-70. [3]. Efficacy, pharmacokinetics, tisssue distribution, and metabolism of the Myc-Max disruptor, 10058-F4 [Z,E]-5-[4-ethylbenzylidine]-2-thioxothiazolidin-4-one, in mice. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2009 Mar;63(4):615-25. |
| Additional Infomation | 10058-F4 is a member of the class of thiazolidinones that is 2-sulfanylidene-1,3-thiazolidin-4-one which is substituted at position 5 by a (4-ethylphenyl)methylidene group. It is a cell permeable inhibitor of c-Myc-Max dimerization and exhibits antitumour effects in vivo. It downregulates c-Myc expression and upregulates CDK inhibitors, p21 and p27 resulting in the inhibition of proliferation, induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in G0/G1 phase. It has a role as an apoptosis inducer and an antineoplastic agent. It is a thiazolidinone and an olefinic compound. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 0.83 mg/mL (3.33 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 8.3 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL of PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL of Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL of normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 0.83 mg/mL (3.33 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 8.3 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 0.83 mg/mL (3.33 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 8.3 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: 2% DMSO +Corn oil : 10 mg/mL (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.0104 mL | 20.0521 mL | 40.1043 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.8021 mL | 4.0104 mL | 8.0209 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4010 mL | 2.0052 mL | 4.0104 mL |